Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS|34 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS)|124 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|38 VideosWAVES
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT & QUESTIONS ANSWERS ( NUMERICAL PROBLEMS. )|48 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER -NUMERICAL PROBLEMS
- A body of mass 0.3 kg is taken up an inclined plane of length 10 m and...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 0.1 kg collides elastically with a ball of unknown mass...
Text Solution
|
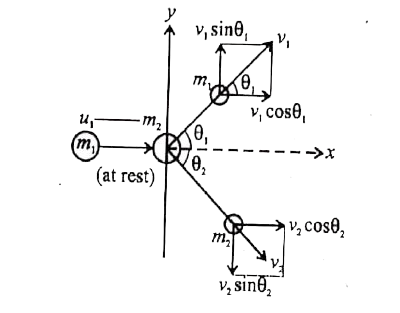
- If a particle elastically collides obliquely with a particle of same m...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate work done from the graph.
Text Solution
|
- What is the stopping distance for a vehicle of mass m moving with spee...
Text Solution
|
- A gardener pushes a lawn roller through a distance of 20m. If he appli...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along the x-axis from x=0 to x=5m under the influence...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet weighing 10g is fined with a velocity of 800ms^(-1). After pa...
Text Solution
|
- A vehicle of mass 15 quintal climbs up a hill 200m high. It then moves...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2kg is resting on a rough horizontal surface. A force o...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2kg is resting on a rough horizontal surface. A force o...
Text Solution
|
- A bolt of mass 0.3 kg falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving dow...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a spring when stretched through a distance x i...
Text Solution
|
- A man weighing 60 kg climbs up a staircase carrying a 20 kg load on hi...
Text Solution
|
- A 10kg ball and 20kg ball approach each other with velocities 20ms^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- A railway carriage of mass 9000 kg moving with a speed of 36kmh^(-1) c...
Text Solution
|
- Two ball bearing of mass m each moving in opposite directions with equ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball falls under gravity from a height of 10m with an initial downwa...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the velocity of the bob of a simple pendulum at its mean pos...
Text Solution
|
- If the KE of a body increases by 300% by what percent will the linear ...
Text Solution
|