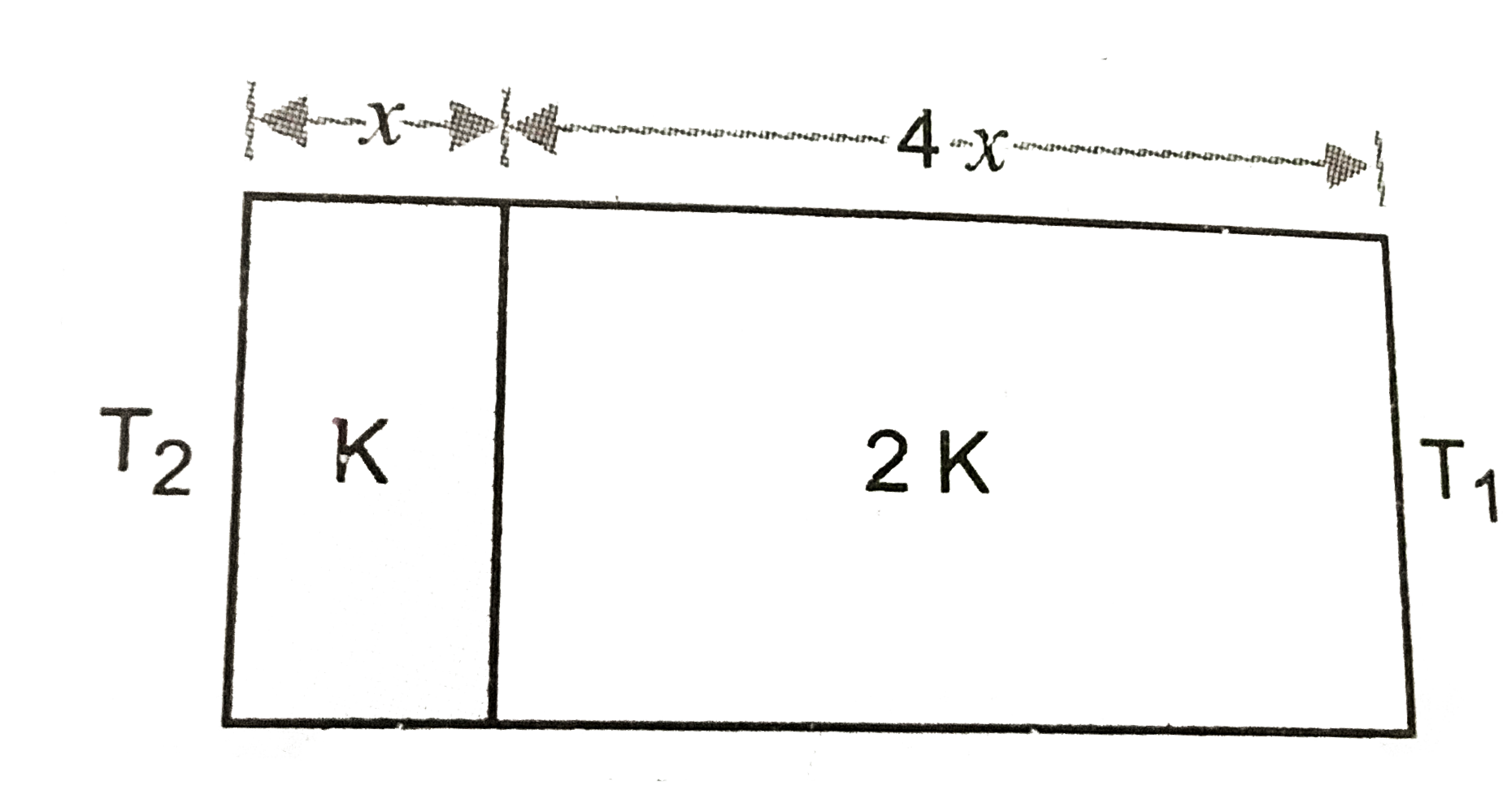
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-EXERCISE -02
- Two plates of equal areas are placed in contact with each other . Thei...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical square rods of metal are welded end to end as shown in f...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of same dimensions are arranged as shown in Fig. They have ...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of the two outer surfaces of a composite slab, consist...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a system of two concentric spheres of radii r1 and r2...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of an ideal gas varies according to the law P = P(0) - AV...
Text Solution
|
- A thermal insulated vessel contains some water at 0^(@)C. The vessel i...
Text Solution
|
- A closed cubical box is made of perfectly insulating material and the ...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical adiabatic containers A, B and C Contain helium, neon a...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose 0.5 moles of an ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion as...
Text Solution
|
- Graph shows a hypothetical speed distribution for a sample of N gas pa...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of an isotropic cubical solid of length l(0), density ...
Text Solution
|
- A glass rod when measured with a zinc scale, both being at 30^(@)C, ap...
Text Solution
|
- Two fines steel wires , fastened between the projectors of a heavy bra...
Text Solution
|
- In a mercury-glass thermometer the cross-section of the capillary port...
Text Solution
|
- 5g of steam at 100^(@)C is mixed with 10g of ice at 0^(@)C. Choose cor...
Text Solution
|
- n moles of an ideal triatomic linear gas undergoes a process in which ...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of gas follow process represented by PV^(2) = constant . Bulk...
Text Solution
|
- Four moles of hydrogen , two moles of helium and one mole of water vap...
Text Solution
|
- A diatomic gas obeys the law pV^x= constant. For what value of x, it h...
Text Solution
|