A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-EXERCISE - 05 (B) (ASSERTION & REASON )
- Statement-1: The total translational kinetic energy of fall the molecu...
Text Solution
|
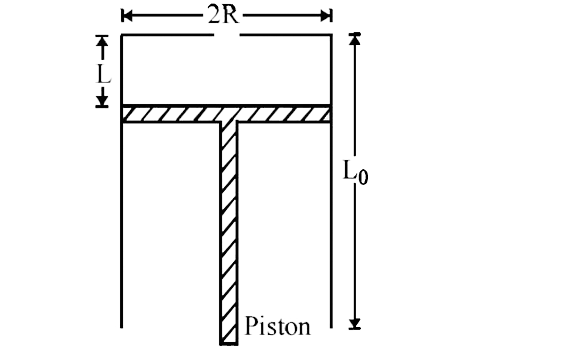
- A fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed thermally conducting cylinder has a radius R and height L0. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas bubble (gamma=5//3) is trapped ...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas bubble (gamma= (5)/(3)) is trap...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical monoatomic ideal gas bubble (gamma=5//3) is trapped ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig., a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) pis...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig., a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) pis...
Text Solution
|
_E01_431_S01.png)