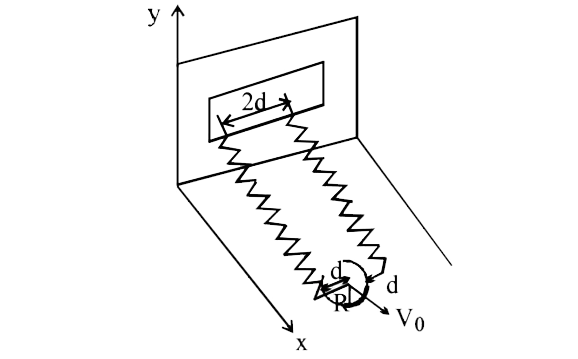
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ALLEN|Exercise Subjective|30 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ALLEN|Exercise Solved Example|3 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ALLEN|Exercise Match The Column|9 VideosRACE
ALLEN|Exercise Basic Maths (Wave Motion & Dopplers Effect) (Stationary waves & doppler effect, beats)|25 VideosTEST PAPER
ALLEN|Exercise PHYSICS|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems