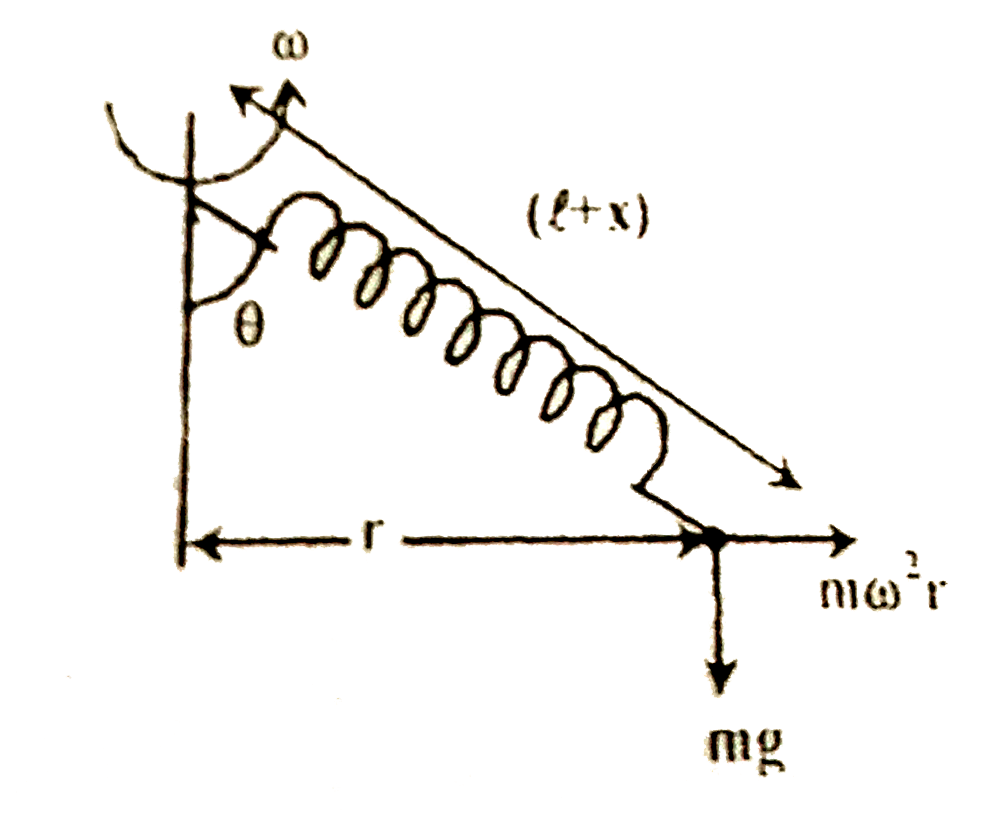
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- A rotor is rotating with a constant angular velocity omega about its o...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile is thrown with a velocity u(0) at an angle theta with the...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is fixed to one end of a light spring of force co...
Text Solution
|
- A force given by the relation F = 8t, acts on a body of mass 2 kg, ini...
Text Solution
|
- The block shown in the figure in is equilibrium. Find acceleration of ...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown figure, the spring balance and string are massless and th...
Text Solution
|
- Find the position of centre of mass of a uniform disc of radius R from...
Text Solution
|
- The blocks B and C in the figure have mass m each. The strings AB and ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the velocity and acceleration of a point like body at...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass M is moving in a circular path of radius 2m. Its sp...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles of masses 1 kg, 2 kg, 3 kg, and 4 kg are situated at th...
Text Solution
|
- U = 2x^(3) - 2x^(3) - 6x^(2) + 5x, where x is in metres and U is the p...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m accelerates uniformly from rest to velocity v(0) in t...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of neglig...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetic energy acquired by a mass m staring from rest under the ac...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass m is connected to a spring of spring constant k and a st...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass 0.25 kg is attached with a string of length 0.25 m. The ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a U- shaped fixed smooth wire over which a bead of mass (m) i...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars P and Q start from a point at the same time in a straight lin...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum tension in the string of a simple pendulum is 1.2 times th...
Text Solution
|