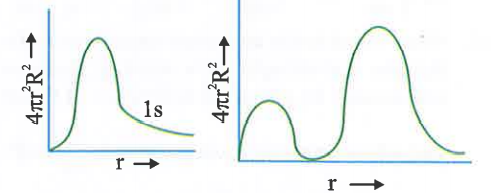
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-ATOMIC STRUCTURE-All Questions
- The Schrodinger wave equation for H-atom is nabla^(2) Psi = (8pi^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The Schrodinger wave equation for H-atom is nabla^(2) Psi = (8pi^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The Schrodinger wave equation for H-atom is nabla^(2) Psi = (8pi^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The hydrogen -like species Li^(2+) is in a spherically symmetric stat...
Text Solution
|
- The hydrogen -like species Li^(2+) is in a spherically symmetric stat...
Text Solution
|
- The hydrogen -like species Li^(2+) is in a spherically symmetric stat...
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen like ion, nucleus has a positive charge Ze, Bohr's quant...
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen like ion, nucleus has a positive charge Ze, Bohr's quant...
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen like ion, nucleus has a positive charge Ze, Bohr's quant...
Text Solution
|
- The value of 'n' of the highest excited state that an electron of hydr...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrogen like species (atomic number Z) is present in a higher excit...
Text Solution
|
- If the lowest energy X-rays have lambda=3.055xx10^(-8) m, estimate the...
Text Solution
|
- Electron in a sample of H- atoms make transitions from state n=x to so...
Text Solution
|
- Aphoton of energy 4.5 eV strikes on a metal surface of work function 3...
Text Solution
|
- Not considering the electronic spin, the degeneracy of the second exci...
Text Solution
|
- In Bohr's model, r(n,z)= radius of n^(th) orbit with atomic number Z ...
Text Solution
|
- {:(Column I,Column II),((A)H,(p)"Radius of"4^(th)"orbit"0.53 xx 4overs...
Text Solution
|
- Match the entries in Column I with the correctly related quantum numbe...
Text Solution
|
- {:(,"ColumnI",,"ColumnII"),((A),"The d-orbital which has two angular n...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|