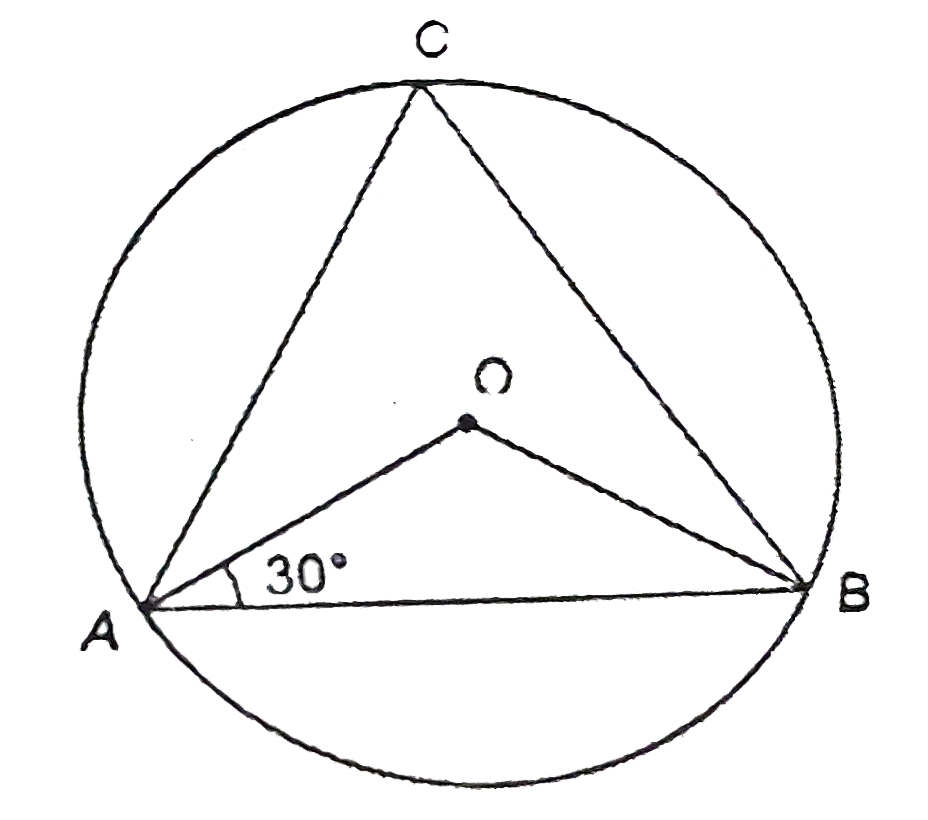
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN-CIRCLE -Revision Exercise (long Answer Questions )
- In the adjoining , O is the centre of the circle. ACB is a segment. If...
Text Solution
|
- A B\ a n d\ C D are two chords of a circle such that A B=6\ c m ,\ ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, P is the centre of the circle. Prove that ang...
Text Solution
|
- Bisectors of angles A ,\ B\ a n d\ C of a triangle A B C interse...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoinig figure, AB is a diameter of the circle, CD is a chord ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, O is the centre of the circle, Then x = ?
Text Solution
|