Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
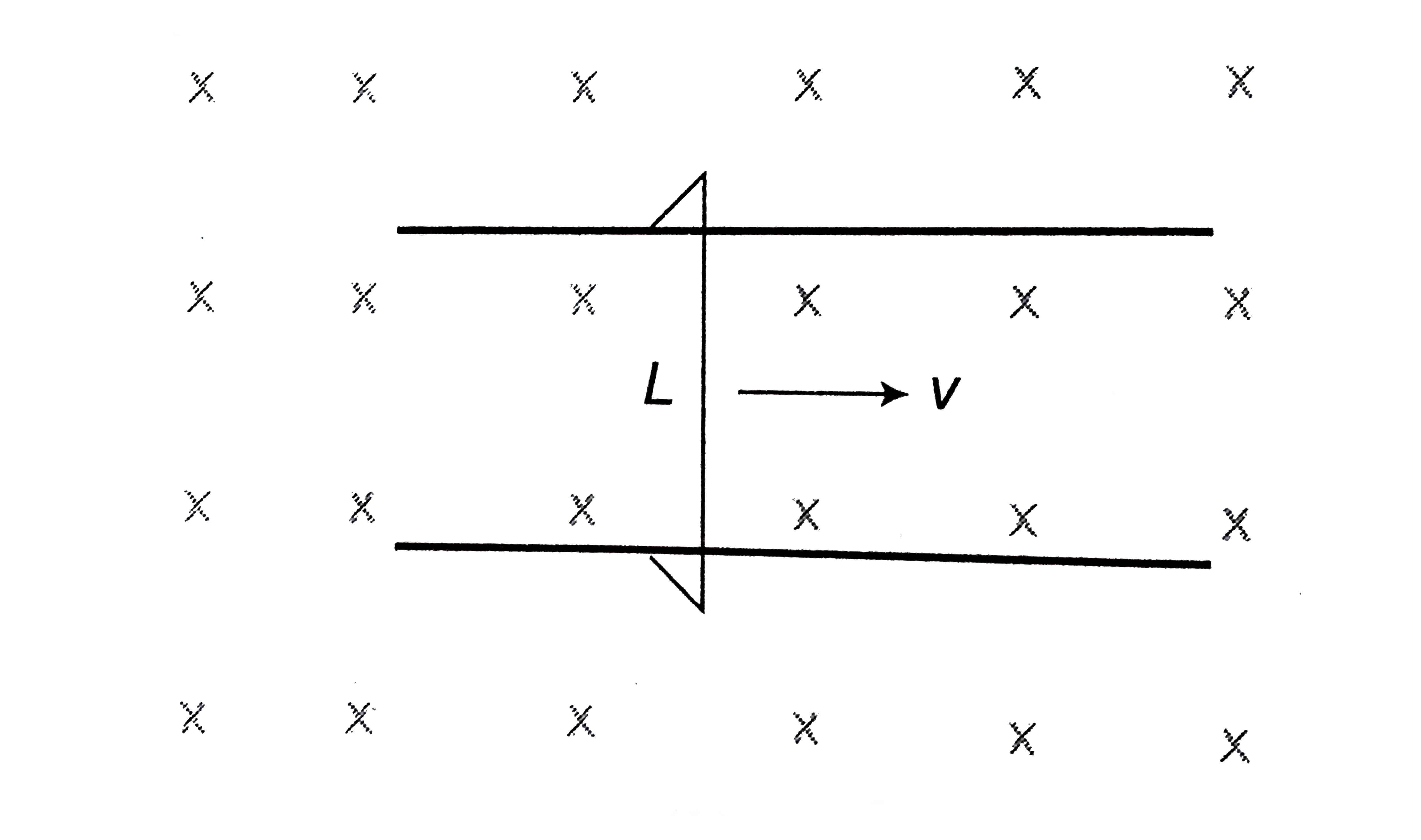
- Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed a...
Text Solution
|
- A straight wire of length l can slide on two parallel plastic rails k...
Text Solution
|
- Consider parallel conducting rails separated by a distance l. There ex...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire xy of lentgh l and mass m is sliding without frictio...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed a...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel conducting rails are separated by a distance L. Two ident...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a wire of resistance R sliding on two parallel, conductin...
Text Solution
|
- A wire having mass m and length 1 can freely slide on a pair or parall...
Text Solution
|
- A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth thic...
Text Solution
|