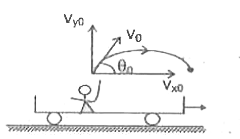
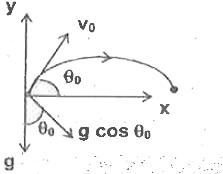
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-KINEMATICS-NUMERICAL BASED QUESTIONS DECIMAL TYPE
- A boy is standing inside a train moving with a constant velocity of ma...
Text Solution
|
- Two highways are perpendicular to each other : imagine them to be alon...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose that water drops are released from a point at the edge of a ro...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a uniform solid regular tetrahedron of mass m...
Text Solution
|
- As part of his discovery of the neutron in 1932, James Chadwick determ...
Text Solution
|
- An object is subjected to an acceleration a = 4 + 3v. It is given that...
Text Solution
|