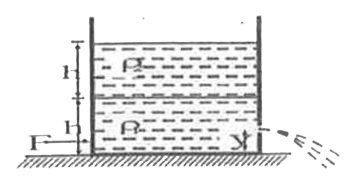
A cylindrical tank having cross - sectional area `A = 0.5 m^(2)` is filled with two liquids of density `rho_(1)= 900 " kg "m^(-3) and rho_(2) = 600 " kg "m^(-3)` , to a height a ` = 6 cm^(2)` is made in right vertical wall at a height y = 20 cm from the bottom . A horizontal force F is applied on the tank to keep it in static equilibrium . The tank is lying on a horizontal surfaces . Neglect mass of cylindrical tank camparison to mass of liquids ( take ` g = 10 ms^(-2)`)
Minimum and maximum values of F to keep the cylinder in static just after the water starts to spill through the hole . If the co - efficient of static friction between contact surfaces is `0.01`
A cylindrical tank having cross - sectional area `A = 0.5 m^(2)` is filled with two liquids of density `rho_(1)= 900 " kg "m^(-3) and rho_(2) = 600 " kg "m^(-3)` , to a height a ` = 6 cm^(2)` is made in right vertical wall at a height y = 20 cm from the bottom . A horizontal force F is applied on the tank to keep it in static equilibrium . The tank is lying on a horizontal surfaces . Neglect mass of cylindrical tank camparison to mass of liquids ( take ` g = 10 ms^(-2)`)

Minimum and maximum values of F to keep the cylinder in static just after the water starts to spill through the hole . If the co - efficient of static friction between contact surfaces is `0.01`

Minimum and maximum values of F to keep the cylinder in static just after the water starts to spill through the hole . If the co - efficient of static friction between contact surfaces is `0.01`
A
0,40 N
B
`5.4 `N , 52.2 N
C
0 , 70 N
D
0, `52.2 ` N
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Total mass of the liquid in the cylinder is
` m = A hrho_(1) +A h rho_(2) = 450 Kg`
Limiting friction ` = mumg = 45 N `
` :. F lt ` limiting friction , therefore , minimum force required is zero .
Consider free body diagram for mximum vertical froces .
N = mg
Now considering horizontal forces ,
N = mg
` F_(max) = F+ muN `
or `F_(max) = 52.2 N `
` m = A hrho_(1) +A h rho_(2) = 450 Kg`
Limiting friction ` = mumg = 45 N `
` :. F lt ` limiting friction , therefore , minimum force required is zero .
Consider free body diagram for mximum vertical froces .
N = mg
Now considering horizontal forces ,
N = mg
` F_(max) = F+ muN `
or `F_(max) = 52.2 N `
Topper's Solved these Questions
FLUID MECHANICS
FIITJEE|Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE II|2 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
FIITJEE|Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE III|2 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
FIITJEE|Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE|2 VideosELECTROSTATICS
FIITJEE|Exercise Example|14 VideosGENERAL PHYSICS
FIITJEE|Exercise MATRIX MATCH TYPE|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A cylindrical tank having cross-sectional area A = 0.5 m^(2) is filled with two liquids of density rho_(1)=900 kg m^(-3) and rho_(2)=600 kgm^(-3) , to a height h=60cm each as shown in the figure. A small hole having area a=5cm^(2) is made in right vertical wall at a height y = 20 cm from the bottom. A horizontal force F is applied on the tank to keep it in static equilibrium. The tank is lying on a horizontal surface. Neglect mass of the cylindrical tank in comparison to mass of the liquids ( ake g = 10 ms^(-2) ). The velocity of efflux is
A cylindrical tank having cross-sectional area A = 0.5 m^(2) is filled with two liquids of density rho_(1)=900 kg m^(-3) and rho_(2)=600 kgm^(-3) , to a height h=60cm each as shown in the figure. A small hole having area a=5cm^(2) is made in right vertical wall at a height y = 20 cm from the bottom. A horizontal force F is applied on the tank to keep it in static equilibrium. The tank is lying on a horizontal surface. Neglect mass of the cylindrical tank in comparison to mass of the liquids ( ake g = 10 ms^(-2) ). The velocity of efflux is
A cylindrical tank having cross-sectional area A = 0.5 m^(2) is filled with two liquids of density rho_(1)=900 kg m^(-3) and rho_(2)=600 kgm^(-3) , to a height h=60cm each as shown in the figure. A small hole having area a=5cm^(2) is made in right vertical wall at a height y = 20 cm from the bottom. A horizontal force F is applied on the tank to keep it in static equilibrium. The tank is lying on a horizontal surface. Neglect mass of the cylindrical tank in comparison to mass of the liquids ( ake g = 10 ms^(-2) ). The velocity of efflux is
A cylindrical tank having cross - sectional area A = 0.5 m^(2) is filled with two liquids of density rho_(1)= 900 " kg "m^(-3) and rho_(2) = 600 " kg "m^(-3) , to a height h = 60 cm^(2) each.A small hole having area a=5 cm^2 is made in right vertical wall at a height y = 20 cm from the bottom . A horizontal force F is applied on the tank to keep it in static equilibrium . The tank is lying on a horizontal surfaces . Neglect mass of cylindrical tank camparison to mass of liquids ( take g = 10 ms^(-2) ) Horizontal force F to keep the cylinder in static equilibrium , if it is placed on a smooth horizontal thrust exerted by fluid jet . But that is equal to mass flowing per second xx change in velocity of this mass :. " " F = (avrho) (v-0) = a rho v^(2) or F = 7.2 N
A cylindrical vessel of a very large cross sectional area is containing two immiscible liquids of density rho_(1)=600kg//m^(3) and rho_(2)=1200kg//m^(3) as shown in the figure. A small hole having cross sectional area 5cm^(2) is made in right side vertical wall as shown. Take atmospheric pressure as p_(0)=10^(5)N//m^(2), g=10m//s^(2) . For this situation mark out the correct statement (s). Take cross sectional area of the cylindrical vessel as 1000cm^(2) . Neglect the mass of the vessel.
A cylindrical tank having cross-sectional area A is filled with water to a height of 2.0 m. A circular hole of corss-section area is opened at a height of 75 cm from the bottom. If a//A=sqrt(0.2, then velocity with which waer emerges from the hole is (g =9.8 ms^(-2))
A cube of 1 kg is floating at the interface of two liquids of density rho_(1) = 3//4 gm//cm^(3) and rho_(2) = 2.5 gm//cm^(3) The cube has (3//5)^(th) part in rho_(2) and (2//5)^(th) part in rho_(1) .Find the density of the cube .
A long cylindrical tank of cross-sectional area 0.5m^(2) is filled with water. It has a small hole at a height 50cm from the bottom. A movable piston of cross-sectional area almost equal to 0.5m^(2) is fitted on the top of the tank such that it can slide in the tank freely. A load of 20 kg is applied on the top of the water by piston, as shown in the figure. Calculate the speed of the water jet with which it hits the surface when piston is 1m above the bottom. (Ignore the mass of the piston)
Two liquids of densities rho_1 and rho_2(rho_2 = 3 rho_1) are filled up behind a square wall of side 6 m as shown in figure. Each liquid has a height of 3 m. The ratio of the forces due to these liquids exerted on upper part MN to that at the lower part NO is (Assume that the liquids are not mixing)2