Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
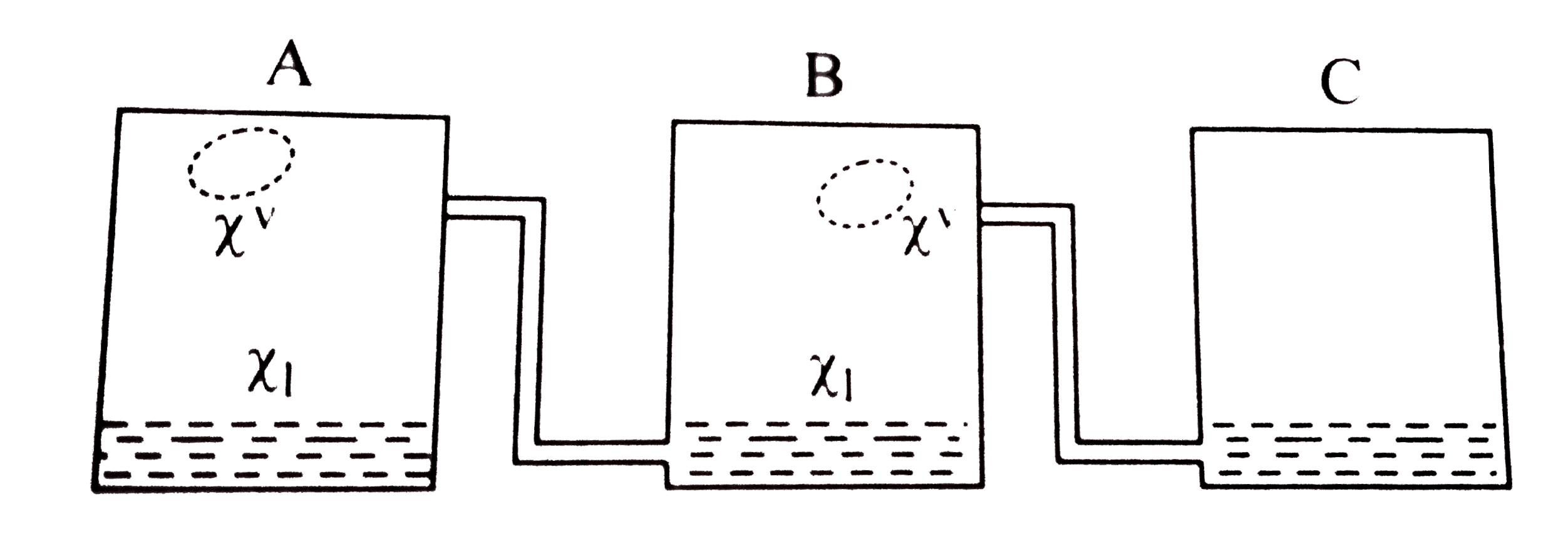
FIITJEE-LIQUID SOLUTION -Single Integer Answer Type Question
- Liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. The vapour pressure of X and ...
Text Solution
|
- 5 litre of a solution contains 25 mg of CaCO(3). What is its concentra...
Text Solution
|
- When 20 g of naphthoic acid (C(11)H(8)O(2)) is dissolved in 50 g of be...
Text Solution
|
- How many grams of a dibasic acid (Mol. Wt. =200) should be present in ...
Text Solution
|
- The amount of urea to be dissolved in 500 cc of water (K(f)=1.86) to p...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the value of any colligative property of KCl solution to ...
Text Solution
|
- 5 litres of a solution contains 25mg of CaCO(3). What is its concentra...
Text Solution
|
- When 20g of naphthoic acid (C(11)H(8)O(2)) is dissolved in 50g of benz...
Text Solution
|
- How many grams of a dibasic acid (Mol. Wt.=200) should be present in 1...
Text Solution
|
- How many grams of urea should be added in 500CC of water (k = 1.86) to...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the value of any colligative property for KCl solution to...
Text Solution
|