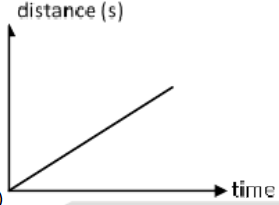
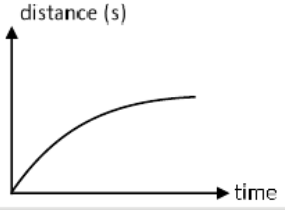
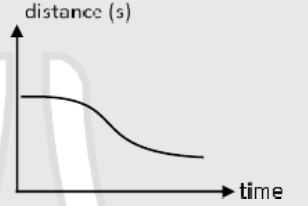
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR-JEE MAIN-All Questions
- Mass density of sphere having radius R varies as rho = rho0(1-r^2/R^2)...
Text Solution
|
- Two light waves having the same wavelength lambda in vacuum are in pha...
Text Solution
|
- Constant power P is supplied to a particle having mass m and initially...
Text Solution
|
- A P-N junction becomes active as photons of wavelength, lambda=400 nm ...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram three point masses 'm' each are fixed at the corners of...
Text Solution
|
- A rod is rotating with angular velocity omega about axis AB. Find cost...
Text Solution
|
- In a diagramatic sphere is a cavity is made it at its centre and now p...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges 4q and -q are kept on x-axis at (-d/2,0) and (d/2,0) resp....
Text Solution
|
- The dimensions of coefficient of thermal conductivity is
Text Solution
|
- Correct order of wavelength of radiowaves, microwaves, xrays, visible ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass M and radius R rotating with speed of omega an...
Text Solution
|
- Short bar magnet is place 30degrees with the external magnetic field 0...
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column
Text Solution
|
- A ball has acceleration of 98(cm)/s^2 in a liquid of density 1g/(cm)^3...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of plane polarized light having flux 10^(-3) Watt falls normall...
Text Solution
|
- Balmer series lies in which region of electromagnetic spectrum
Text Solution
|
- If a ball A of mass mA = m/2 moving along x-axis collides elastically ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider on object of mass m moving with velocity v0 and all other mas...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires A & B bend like as shown in figure. 'A' has radius 2 cm and ...
Text Solution
|
- For lyman series lambdamax -lambdamin = 340 Angstrom . Find same for p...
Text Solution
|