Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
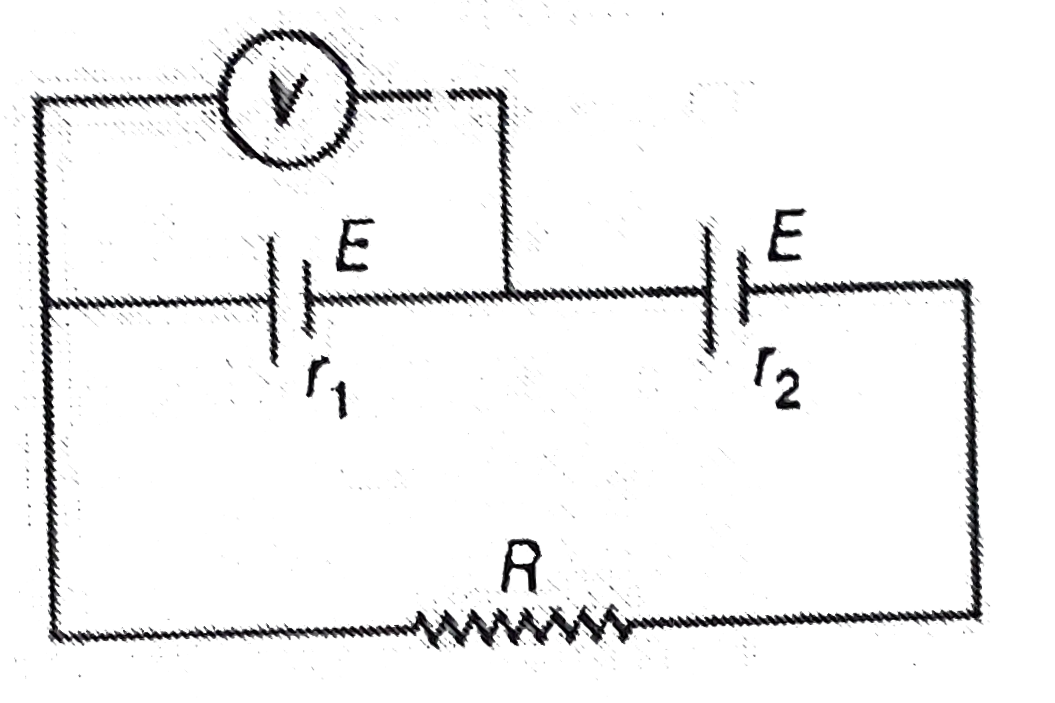
- In the following figure, the reading of an ideal voltmeter V is zero. ...
Text Solution
|
- In the, Ohm's law experiment ot find resistance of unknown resistor R,...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter of resistance R(V) and an ammeter of resistance R(A) are c...
Text Solution
|
- The power dissipated in resistor R(3) shown in the figure is 15 W. The...
Text Solution
|
- The power dissipated in resistor R(3) shown in the figure is 15 W. The...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of same emf epsilon , but different internal resistances r(1...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure, the reading of an ideal voltmeter V is zero. ...
Text Solution
|
- A cell of e.m.f. 2V and negligible internal resistance is connected to...
Text Solution
|
- Let V and I be the readings of the voltmeter and the ammeter respectiv...
Text Solution
|