Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
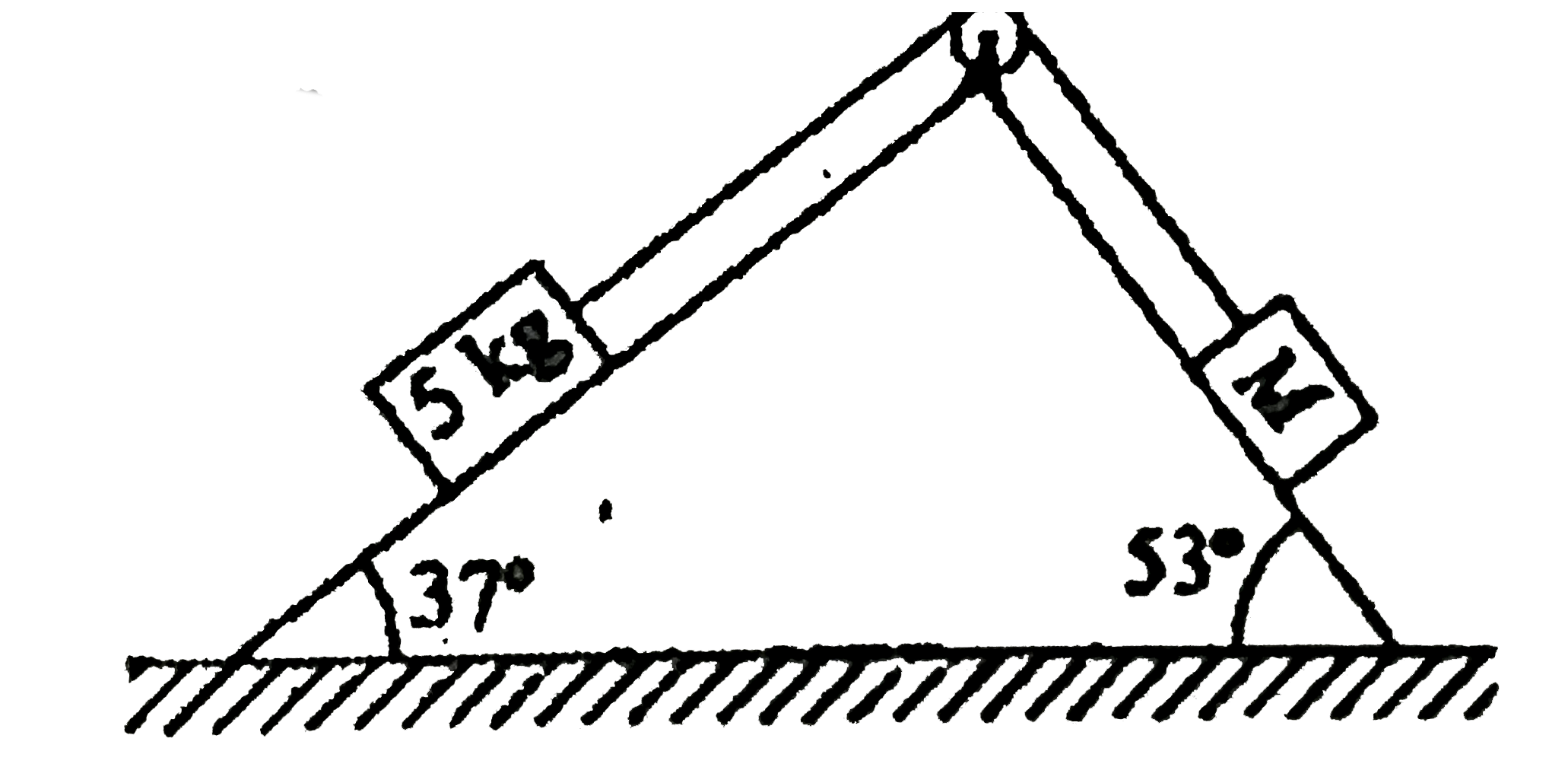
- For what value of M will the masses be in equilibrium. Masses are plac...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure a wedge is fixed to an elevator moving upwards...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed at rest on a smooth wedge of mass M placed...
Text Solution
|
- Block A of mass m is placed over a wedge of same mass m. Both the bloc...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination theta & m...
Text Solution
|
- For what value of M will the masses be in equilibrium. Masses are plac...
Text Solution
|
- Coefficient of friction between block of mass m and fixed wedge is mu ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is placed at rest on the top of a smooth wedge of...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m resting on a wedge of angle theta as shown in the f...
Text Solution
|