Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD-Electric Charges And Field
- Refer to the arrangement of charges in Fig and a Gaussian surface of r...
Text Solution
|
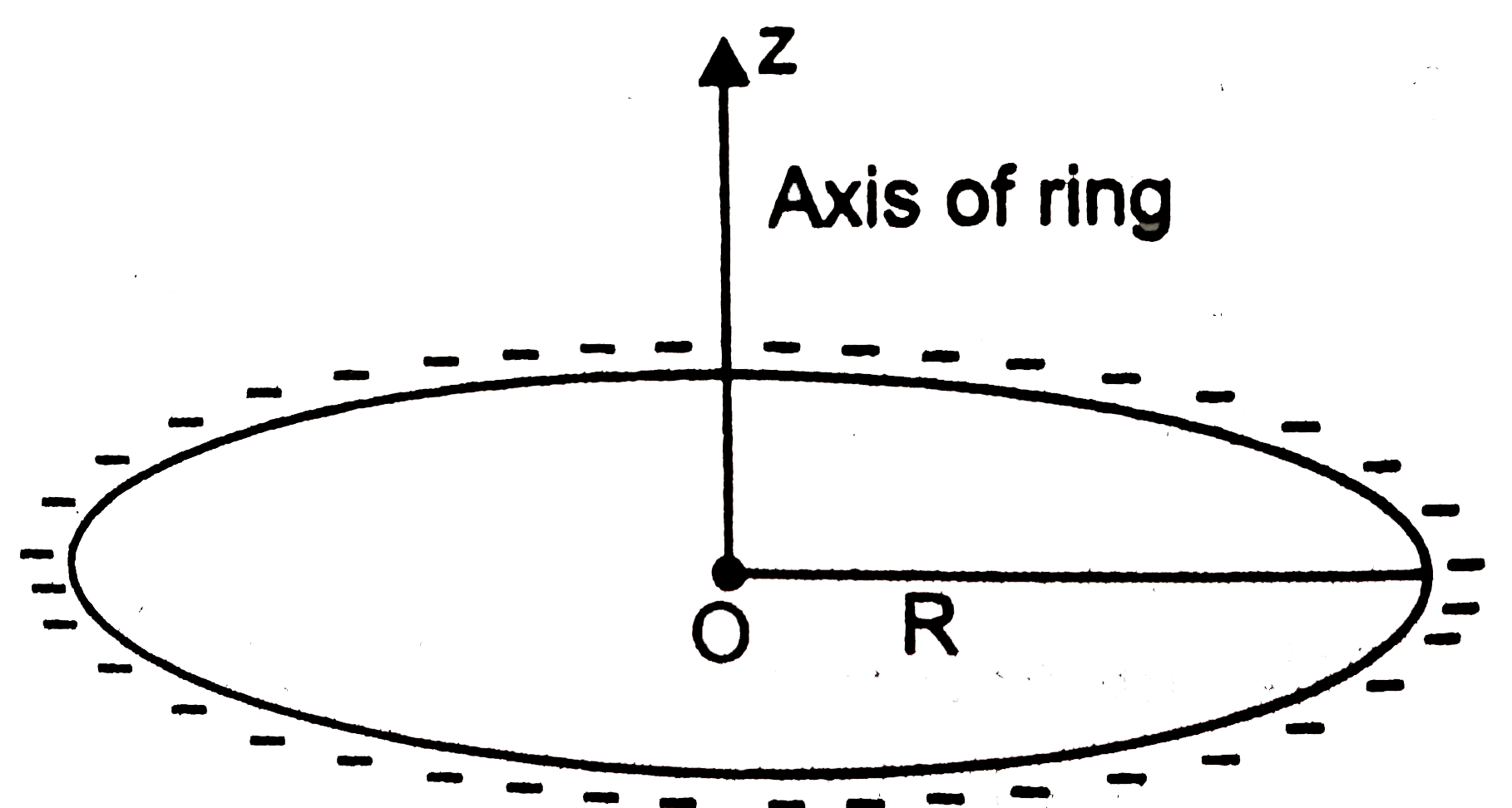
- A positive charge Q is uniformly distributed along a circular ring of ...
Text Solution
|
- An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux thro...
Text Solution
|
- A metal spherical shell has an inner radius R(1) and outer radius R(2...
Text Solution
|
- The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus there ...
Text Solution
|
- If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch the electric field lines for a unifomly charged hollow cylinder...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the total flux through the faces of the cube, with side o...
Text Solution
|
- A paisa coin is made up Al-Mg alloy and weighs 0.75 g. It has a squar...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a coin, It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts...
Text Solution
|
- Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charge q and –3q are placed fixed on x–axis separated by distance ...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows the electric field lines around three points charges A,B,C....
Text Solution
|
- Five charges , q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon ...
Text Solution
|
- In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the univer...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as rho ...
Text Solution
|
- Two fixed, identical conducting plates (alpha and beta), each of surfa...
Text Solution
|
- There is another useful system of units, besides the SI/MKS. A system,...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges -q each are fixed separated by distance 2d. A third charge...
Text Solution
|
- Total charge -Q is uniformly spread along length of a ring of radius R...
Text Solution
|