Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
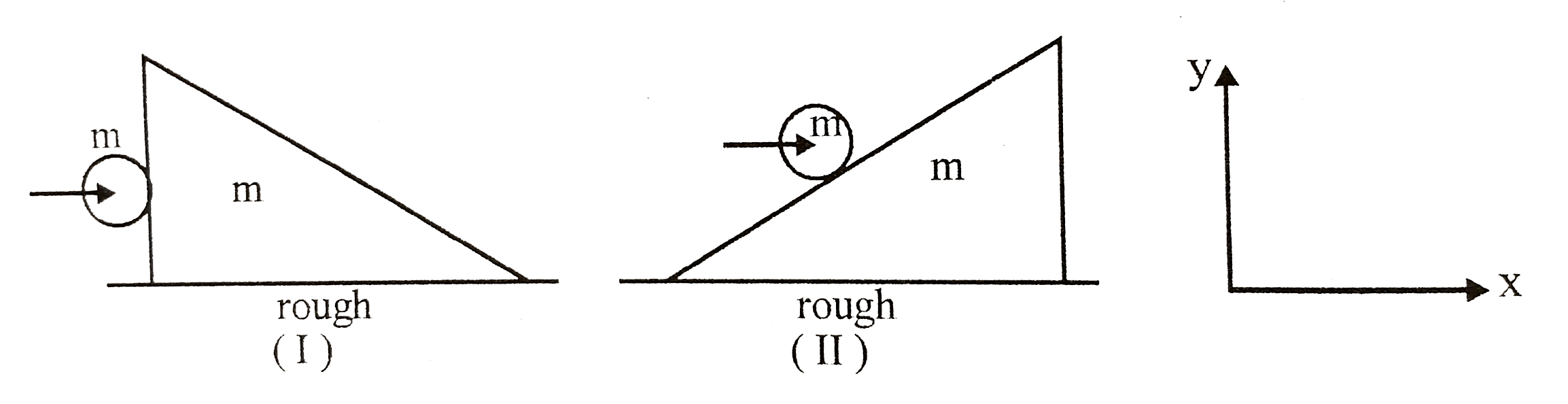
- A ball of mass m collides horizontally with a stationary wedge on a ro...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving horizotally which velocity u hits a wedge of m...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass in collides horizontally with a stationary wedge on a r...
Text Solution
|
- In the given the wedge is acted upon by a constant horizontal force 'F...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m collides horizontally with a stationary wedge on a ro...
Text Solution
|
- A wedge mass m rest on horizontal surface. The inclination of the wedg...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m collides horizontally with a stationary wedge on a ro...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving vertically down , collides with inclined surfa...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown is released from rest. Mass of ball is m kg and that ...
Text Solution
|