Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
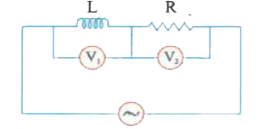
- A pure inductor and a pure resistor are connected in series and an ac ...
Text Solution
|
- Voltmeters V(1) and V(2) are connected in series across a D.C. line V(...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor and an inductor are conneted in sires to a 220 "volt" AC su...
Text Solution
|
- A 500 Omega resistor and a capacitor C are connected in series across ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal choke coil takes a current fo 8 ampere when connected to an A...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor R is connected in series with a coil. The system is subjec...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown in the figure, the cell is ideal. The readi...
Text Solution
|
- In an LCR series circuit, the reading of ideal voltmeters V(1) and V(2...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure, two resistors R(1) and R(2) have b...
Text Solution
|