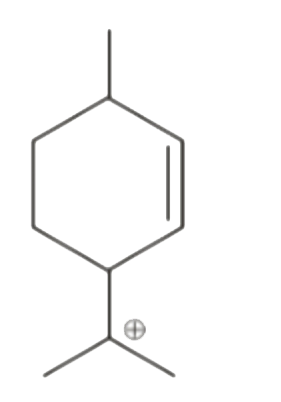
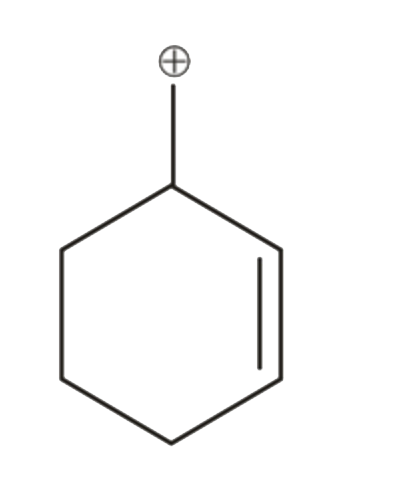
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA NEET TEST 103-CHEMISTRY
- Which of the following change represents a disproportionation reaction...
Text Solution
|
- The compound which does not react with sodium is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocation can not undergo rearrangement ?
Text Solution
|
- For two gases, A and B with molecular weights M(A) and M(B). It is obs...
Text Solution
|
- Formaldehyde reacts with excess of ammonia to give
Text Solution
|
- When CO2 is passed through brine solution , saturated with ammonia, wh...
Text Solution
|
- Which arrangement of electrons leads to ferromagnetism ?
Text Solution
|
- Which oxide of carbon is formed when malonic acid is warmed with P(2)O...
Text Solution
|
- Saccharin is imide of
Text Solution
|
- AsF5 reacts with XeF4 to form an adduct. The shapes of cation and anio...
Text Solution
|
- For the gaseous reaction C2H4 + H2 <implies C2H6 The equilibrium c...
Text Solution
|
- If the K(a) value in the hydrolysis reaction, B^(+) + H(2)O to BOH + H...
Text Solution
|
- Dehydration of alcohol into alkene by concentration H2SO4 involves whi...
Text Solution
|
- What is the name of the complex [Al(OH)(2)(H(2)O)(4)]SO(4) ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is an incorrect statement ?
Text Solution
|
- Standard molar enthalpy of formation of CO(2) is equal to :
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent conductivity of 0.1 M weak acid is 100 times less than ...
Text Solution
|
- H2O has net dipole moment while BeF2 has zero dipole moment because
Text Solution
|
- 0.50g sample of impure CaCO3 is dissolved in 50 ml of 0.0985 (N) HCl. ...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following redox reaction precipitate is not formed?
Text Solution
|