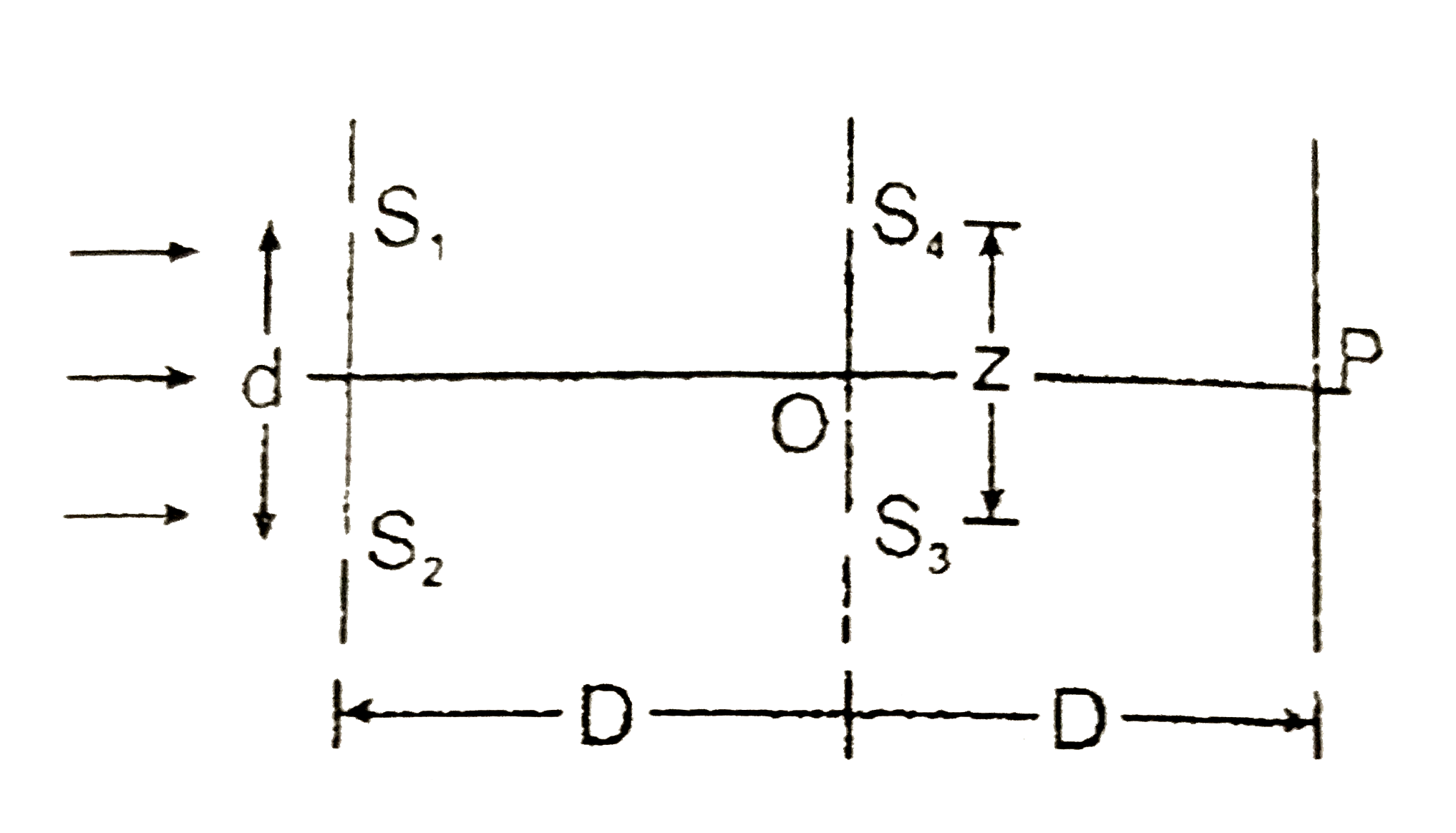
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-WAVE OPTICS-Exercise-2 (Part-2)
- Figure shows two coherent sources S(1)-S(2) vibrating in same phase. A...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown three slits s(1),s(2) and s(3) are illuminated wit...
Text Solution
|
- Parallel monochromatic beam is falling normally on two slits S(1) and ...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow monochromatic beam of light of intensity I is incident on a g...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's experiment, the upper slit is covered by a thin glass pla...
Text Solution
|