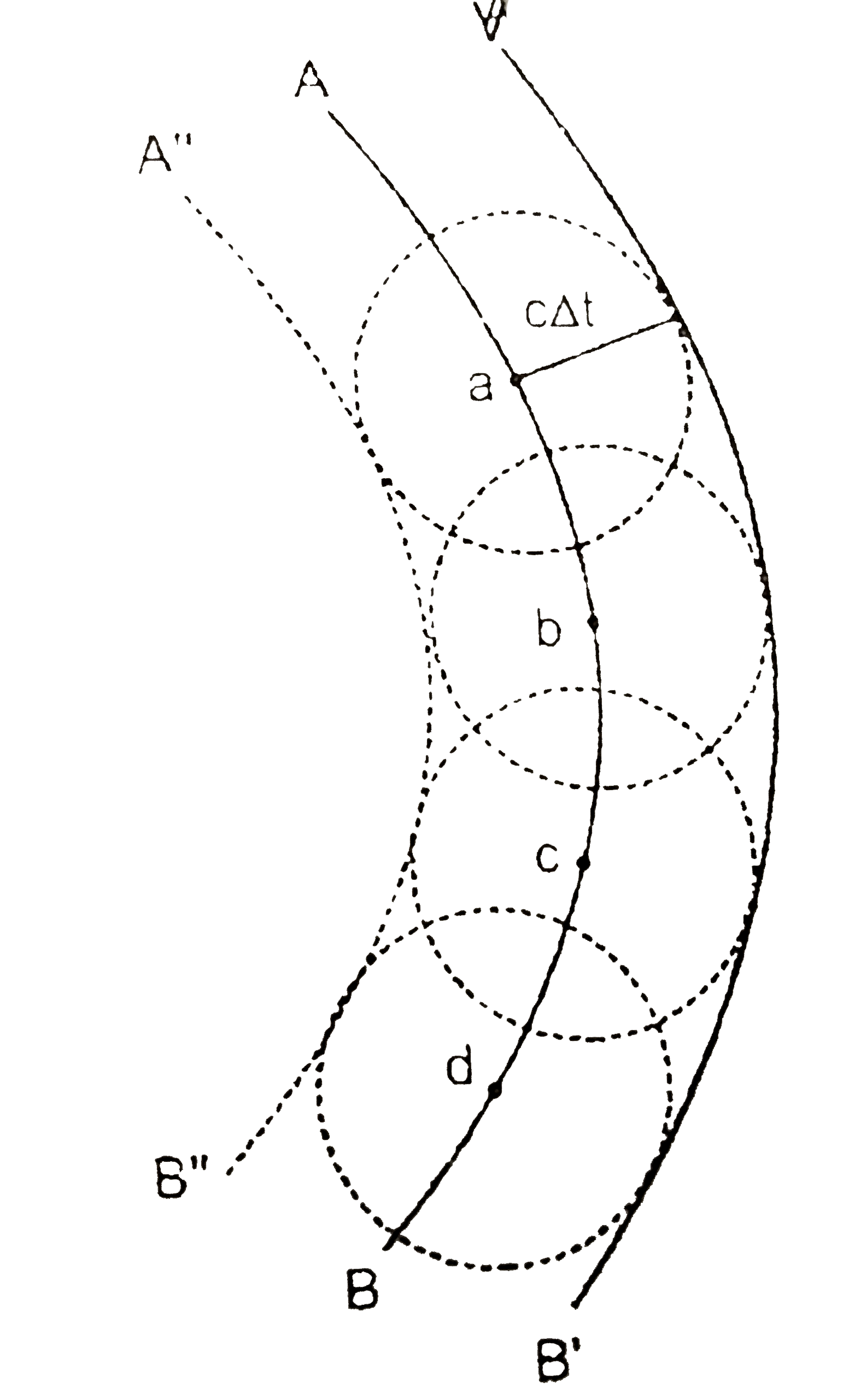
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-WAVE OPTICS-Exercise-3 (Part-3)
- What is is plane polarised light ? Two polaroids are placed at 90^(@) ...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by a linearly polarised light? Which type of waves can b...
Text Solution
|
- How is a wavefront defined ? Using Hygen's construction draw a figure ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Light, from a sodium lamp, is passed through two polaroid sheets P...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment , the slits are Kept 2mm apart and...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment ,momochromatic light of wavelength 6...
Text Solution
|
- In a single slit diffraction experiment when a tiny circular obstacle ...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram, given below, shows the refracton of a plane wavefront, in...
Text Solution
|
- How would the angular separation of interference fringes in Young's do...
Text Solution
|
- Two polaroid A and B are set in crossed positions. A third polaroid C ...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment , the two slits 0.20 mm apart are il...
Text Solution
|
- State Huygens' principle of diffraction of light.
Text Solution
|
- State the importance of coherent sources in the phenomenon of interfer...
Text Solution
|
- (a) What is a wave front?How does it propagate?Using Huygens' principl...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Define a wavefront. Use Huygen' principle to shown diagrammaticall...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why are coherent sources necessary to produce a sustained interfer...
Text Solution
|
- (a) In Young's double slit experiment, derive the condition for (i) co...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following waves can be polarized (i) Heat (ii) Sound wave...
Text Solution
|
- Two wavelength of sodium light 590 nm and 596 nm are used, in turn, to...
Text Solution
|
- (a) In Young's double slit experiment, describe briefly how bright and...
Text Solution
|