Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-ELECTROCHEMISRY-Advanced Level Problems
- Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell Pt|H(2)(1.0atm)|CH(3)COOH (0.1M)||N...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of all ions in an ideal soluti...
Text Solution
|
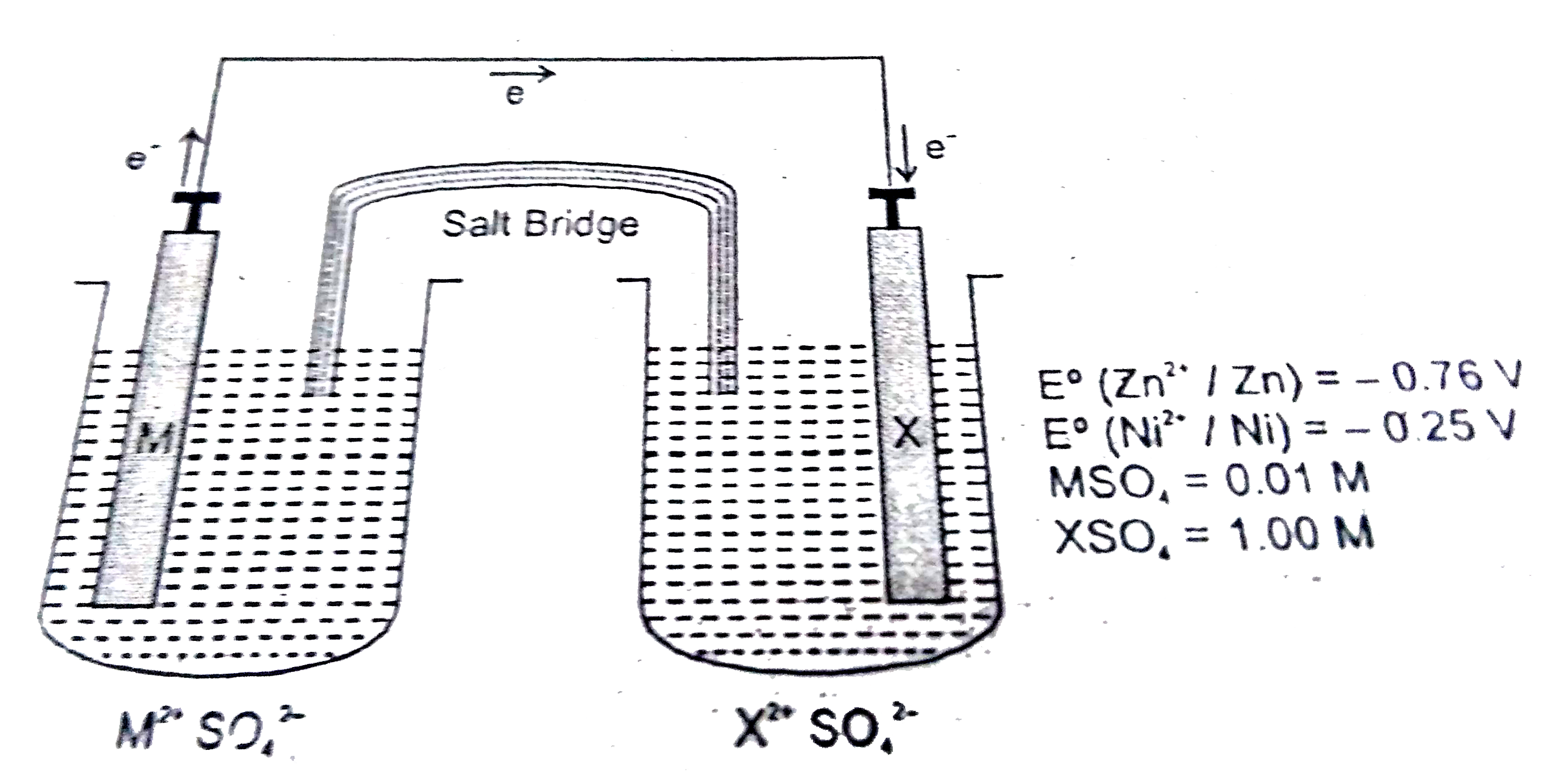
- The expermental setup for a typical Zn-Ni galvanic cell as shown below...
Text Solution
|
- At 18^(@)C the mobilities of NH(4)^(+) and CIO(4)^(-) ions are 6.6 xx ...
Text Solution
|
- 10g fairly concentrated solution of CuSO(4) is electrolyzed using 0.01...
Text Solution
|
- An electric current is passed through electrolytic cells in series one...
Text Solution
|
- After electrolytes of NaCl solution with inert electrodes for a certai...
Text Solution
|
- Same quantity of charge is being used to liberate iodine (at anode) an...
Text Solution
|
- The resistance of two electrolytes X and Y ere found to be 45 and 100 ...
Text Solution
|
- For 0.0128 N solution fo acetic at 25^(@)C equivalent conductance of t...
Text Solution
|
- Specific conductance of pure water at 25^(@)C is 0.58 xx 10^(-7) mho c...
Text Solution
|
- The reduction potential diagram for Cu in acid solution is : Calc...
Text Solution
|
- For the cells in opposition, Zn(s) | ZnCl(2)(sol).|AgCl(s)|Ag|AgCl(s...
Text Solution
|
- At Tl^(+) |Tl couple was prepared by saturating 0.1 M KBr with TlBr an...
Text Solution
|
- The following two cells with initial concentration as given are connec...
Text Solution
|
- For the cell (at 1bar H(2) pressure) Pt|H(2)(g) HX(m(1), NaX(m(2), NaC...
Text Solution
|
- A positive potential implies that the species under study has reductio...
Text Solution
|
- In a galvanic cell, the half-cell having more standard potential serve...
Text Solution
|
- At 300 K specific conductivity of ethanol is 4xx10^(-10)mhocm^(-1). Th...
Text Solution
|
- Metallic sodium cannot be prepared from electrolysis of an aqueous sol...
Text Solution
|