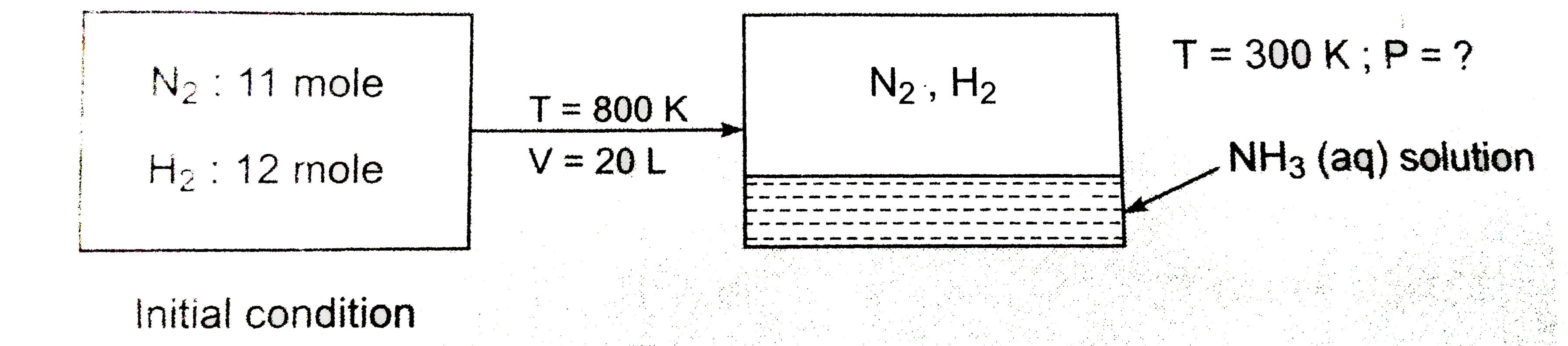Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- 11 moles of N(2) and 12 moles of H(2) mixture reacted in 2.0 litre ves...
Text Solution
|
- A100dm^(3) flask contains 10 mole each of N(2) and H(2) at 777 K. Afte...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid A at 300K is 577 Torr and that of p...
Text Solution
|
- One litre of a gaseous mixture of two gases mixture of two gases effus...
Text Solution
|
- 11 moles of N(2) and 12 moles of H(2) mixture reacted in 2.0 litre ves...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gaseous mixture of ethane (C(2)H(4)) and (C(2)H(4)) occupies ...
Text Solution
|
- एक मिश्रण में H(2) तथा Br(2) के समान मोल मिलाये गये है | अभिक्रिया के ...
Text Solution
|
- एक गैसीय मिश्रण में N(2),O(2) और NO क्रमशः 2, 4 और 3 मोल हैं। यदि मिश्...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of pure liquid (A) at is 575 torr and that of pure...
Text Solution
|