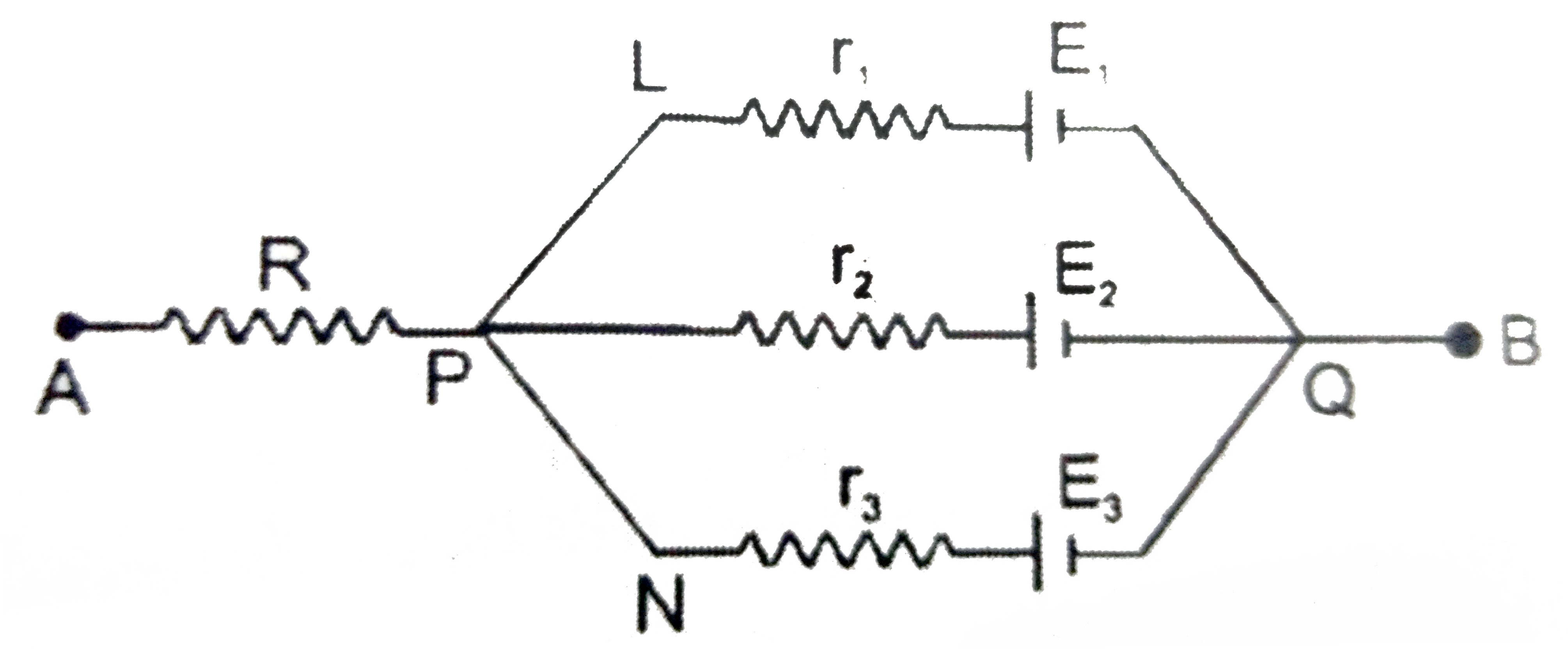
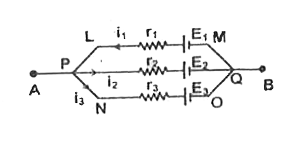
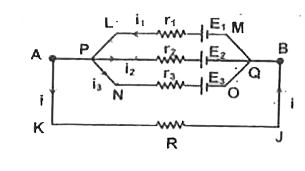
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE)|10 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS (OBJECTIVE)|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
FIITJEE|Exercise Comprehension -4|3 VideosCOLLISION
FIITJEE|Exercise (NUMERICAL BASED QUESTIONS)|4 VideosELASTICITY AND WAVES
FIITJEE|Exercise Assignment Problems (Objective) Level-II|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-CURRENT ELECTRICITY- Illustration
- Find the equivalent resistance between A and B in the circuit shown he...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a source (a battery) with an emf E of 12 V with an in...
Text Solution
|
- If in the previous problem the battery is being charged with a current...
Text Solution
|
- in the circuit shown in the figure, each battery is of 5 V and has an ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. E(1)=3" volt",E(2)=2" volt",E(3)=1" vole ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the values of currents ·I(1)I(2)I(3)andI(4) Is and loin the ...
Text Solution
|
- A part of a circuit in steady state along with the currents flowing in...
Text Solution
|
- A potentiometer wire of length 100 cm has a resistance of 100Omega it ...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer has a resistance of 30 ohm and a current of 2 mA is nee...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor C (=100 muF) is charged with a total charge of 1.2 xx 10^(...
Text Solution
|