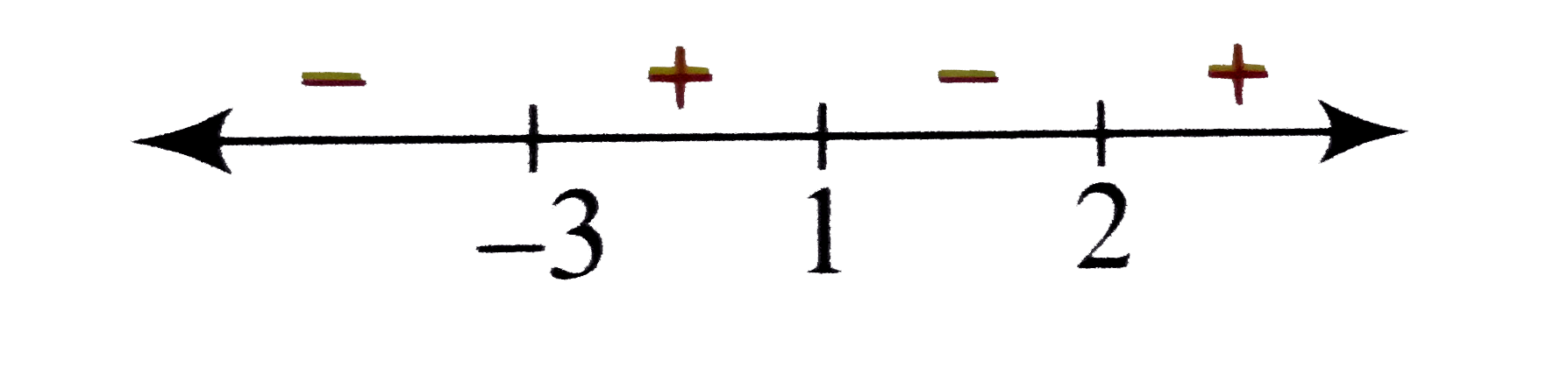
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS-Exercise
- Find the values of p for which the equation x^(4)-14x^(2)+24x-3-p=0 ha...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=(x-1)(x^(2)-x+1).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=(x^(2)-x^(5))(x-2)^(3).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graphs of (i) y=x^(2)(x-1)|x-2| (ii) y=x^(3)(x-1)|x-2|
Text Solution
|
- Write a possible rational function f that has a vertical asymptote at ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=f(x)=(x^(2))/(x^(2)+1).
Text Solution
|
- Draw graph of y=(x^(2)-6x+4)/(x^(2)+2x+4).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of f(x)=(x^(2)-8x+15)/(x^(2)-2x).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of f(x)=(5x^(2))/((x-1)^(3)).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the graph of y=x+1/x
Text Solution
|
- Draw graph of y=(1)/(x^(2))-x.
Text Solution
|
- Draw graph of y=(x^(3)-2x^(2))/(3(x+1)^(2)).
Text Solution
|
- Draw graph of y=(x^(3)-5x)/(x^(2)+1).
Text Solution
|
- Given C(1) lt C(2) lt C(3) lt C(4) lt C(5) and the function y=f(x) is ...
Text Solution
|