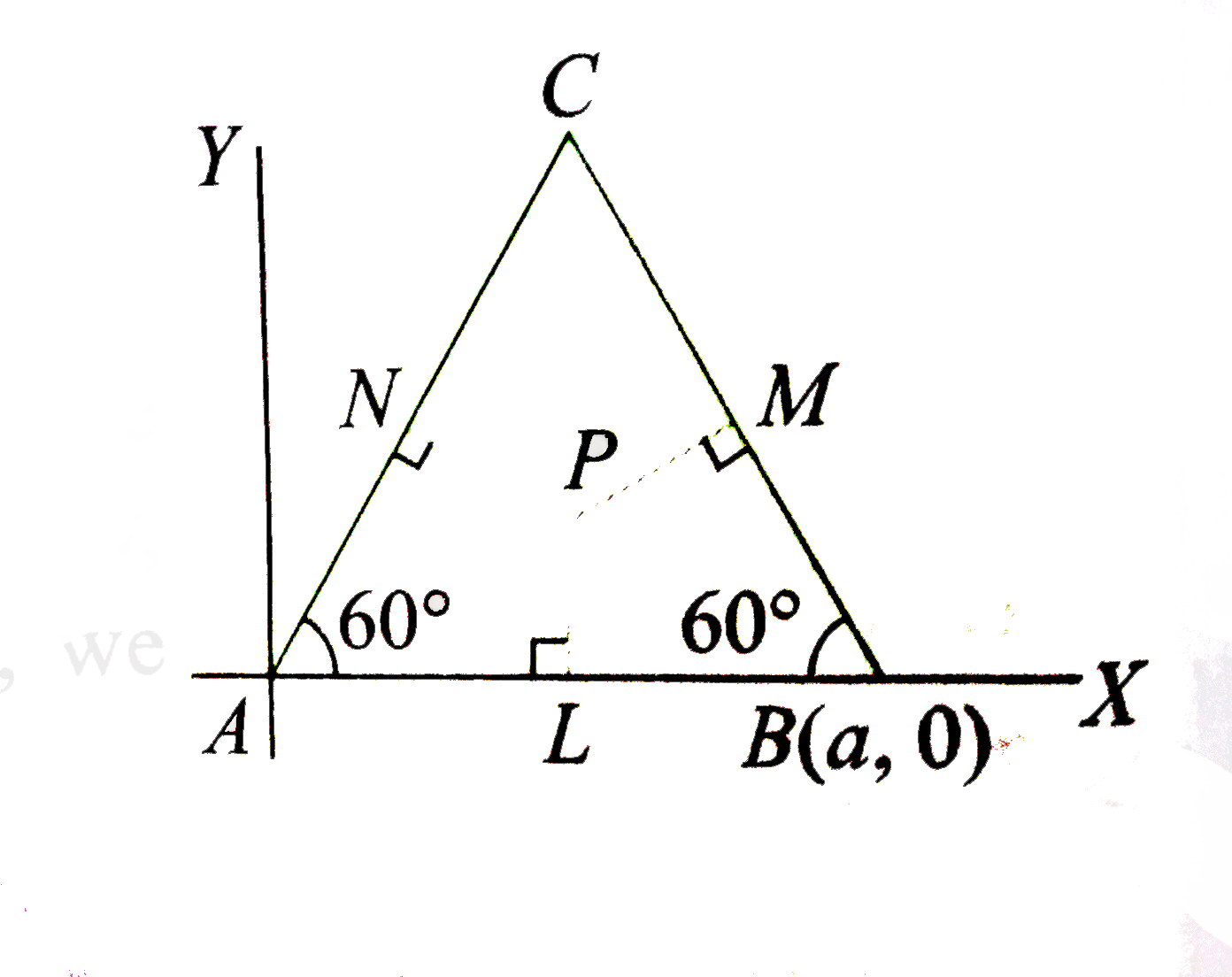Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-STRAIGHT LINES-JEE Advanced Previous Year
- A B C is an equilateral triangle with A(0,0) and B(a ,0) , (a>0). L, M...
Text Solution
|
- The locus of the orthocentre of the triangle formed by the lines (1+p)...
Text Solution
|
- A straight line L through the point (3,-2) is inclined at an angle 60^...
Text Solution
|
- For a gt b gt c gt 0, if the distance between (1,1) and the point of i...
Text Solution
|
- For a point P in the plane, let d1(P)a n dd2(P) be the distances of th...
Text Solution
|