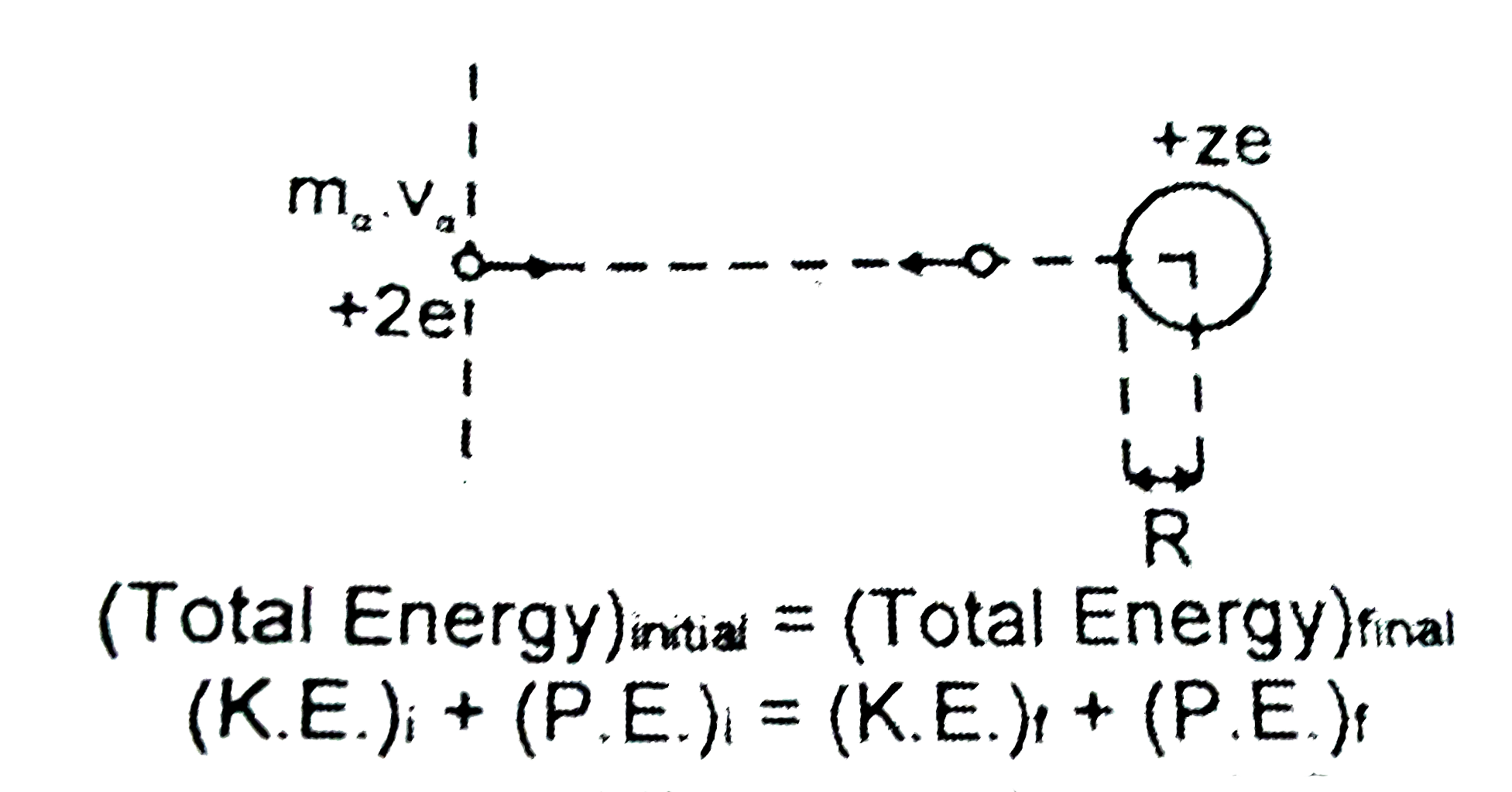A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DPP-QUESTIONS
- Which of the following pairs has different values of e/m:
Text Solution
|
- As an electron (at rest) is brought towards a proton from infinity, it...
Text Solution
|
- Rutherford model: The approximate size of the nucleus can be calculate...
Text Solution
|
- If the diameter of two different nuclei are in the ratio 2: 1, then ca...
Text Solution
|
- For a broadcasted electromagnetic wave having frequency of 1200 KHz, c...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the ratio of the energy of a photon of wavelength 3000 Å to ...
Text Solution
|
- What volume (in mL) of liquid H2O2 has same number of molecules as the...
Text Solution
|
- If the atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) of an element X are relat...
Text Solution
|
- If the frequency of violet radiation is 7.5xx10^14 Hz, then the value ...
Text Solution
|
- A photon of 300 nm is absorbed by a gas and then re-emits two photons...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct statement(s)
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following conditions the de Broglie wavelength of part...
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct statement
Text Solution
|
- What change in molar energy (in J) would be associated with an atomic ...
Text Solution
|
- For a wave frequency is 10 Hz and wavelength is 2.5 m. How much distan...
Text Solution
|
- A certain dye absorbs 4000 Å and fluoresces at 8000 Å. These being wav...
Text Solution
|
- In Rutherford formula, maximum number of a-particles deflecting is for...
Text Solution
|
- If the volume of nucleus of an atom V is related to its mass number A ...
Text Solution
|
- Photon of which light has minimum energy
Text Solution
|
- Visible spectrum contains light of following colours ''Violet - Indigo...
Text Solution
|