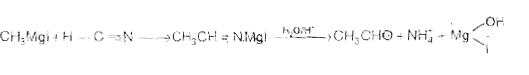Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Give chemical equations and name the main product formed when (i) Et...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when: (i). Methyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KC...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) chlorobenzene is treated with Cl(2)//FeCl(3) (ii...
Text Solution
|
- Give chemical equations and name the main product formed when (i) Et...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) Propanone is treated with methylmagnesium iodide...
Text Solution
|
- The products formed when ethyl chloride is treated with silver cyanide...
Text Solution
|
- When n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic potash, the main produ...
Text Solution
|
- The products form when ethyl chloride is treated with AgCN, are
Text Solution
|
- The products form when ethyl chloride is treated with AgCN, are
Text Solution
|