A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- Find acceleration of 5kg bock. All stirng and pulley are ideal. (g=10m...
Text Solution
|
- Find maximum compression is the spring from the given figure.
Text Solution
|
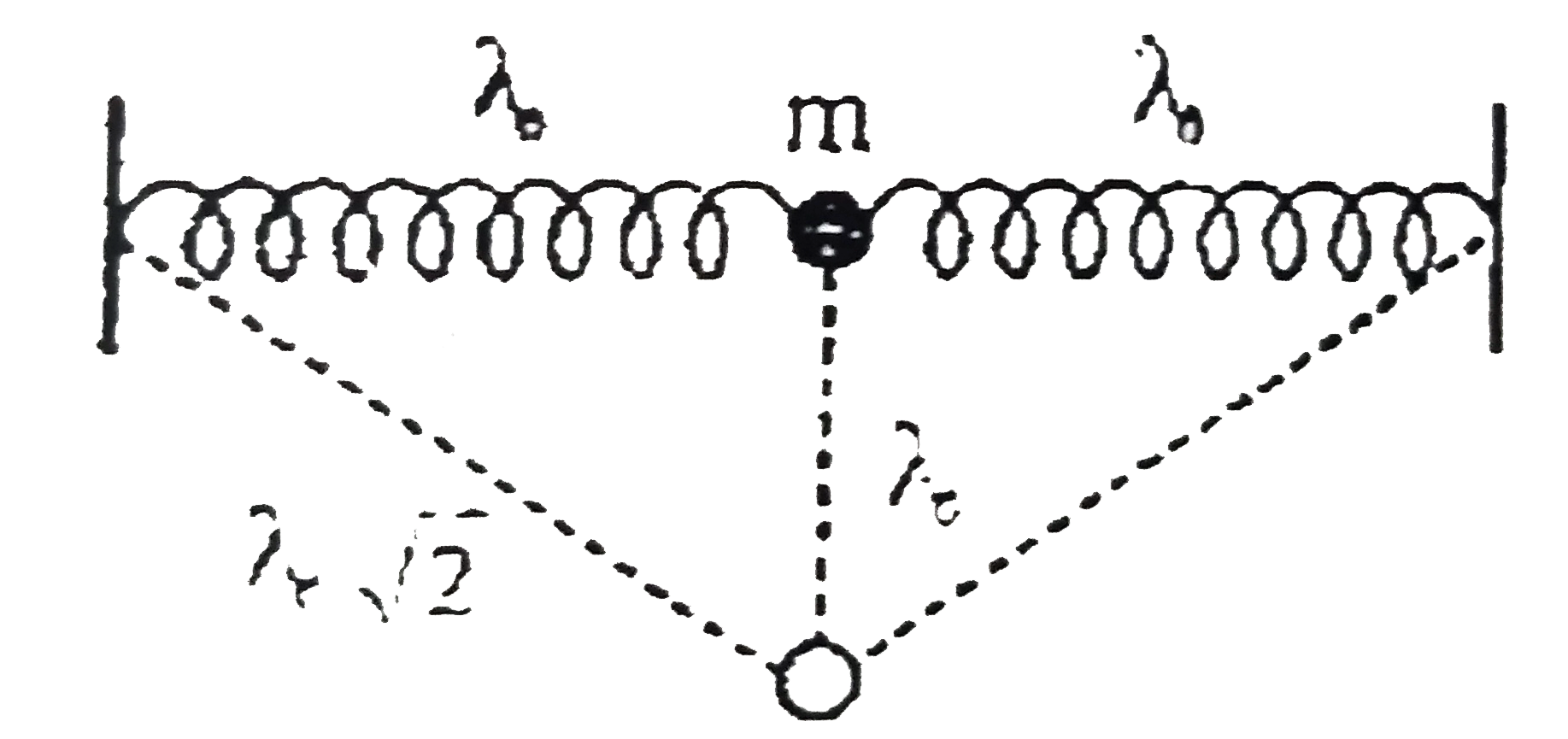
- A small bob joins two light unstretched identical springs anchored at ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle start motion from rest with constant tangential acceleratio...
Text Solution
|
- The value of angle such that the acceleration of A is g/6 downwards al...
Text Solution
|
- Work done by kinetic friction can be
Text Solution
|
- A person is standing on a escalator which is moving up uniformly. Find...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2kg start motion form rest on a circular path of ra...
Text Solution
|
- A boat is heading towards North with velocity 10ms^(-1) with respect t...
Text Solution
|
- An object is thrown at an angle 60^(@) above horizontal with velocity ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball weighing 10g hits a hard surface vertically with a speed of 5m/...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P moves in a circular path of radius R, with centre at O at...
Text Solution
|
- A man standing on flat car under the shed of a small umbrella as shown...
Text Solution
|
- A man drags a box of mass 20kg on a horizontal floor as shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- Delhi is at latitude 30^(@)N longitude 78.5^(@) E. if the angular velo...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular ring of mass per unit length p and radius r is rotatin...
Text Solution
|
- An apple of mass 0.5 kg is swing around on a string in a circle in a h...
Text Solution
|
- An apple of mass 0.5 kg is swing around on a string in a circle in a h...
Text Solution
|
- An apple of mass 0.5 kg is swing around on a string in a circle in a h...
Text Solution
|
- Four forces act on a point object. The object will be in equilibrium, ...
Text Solution
|