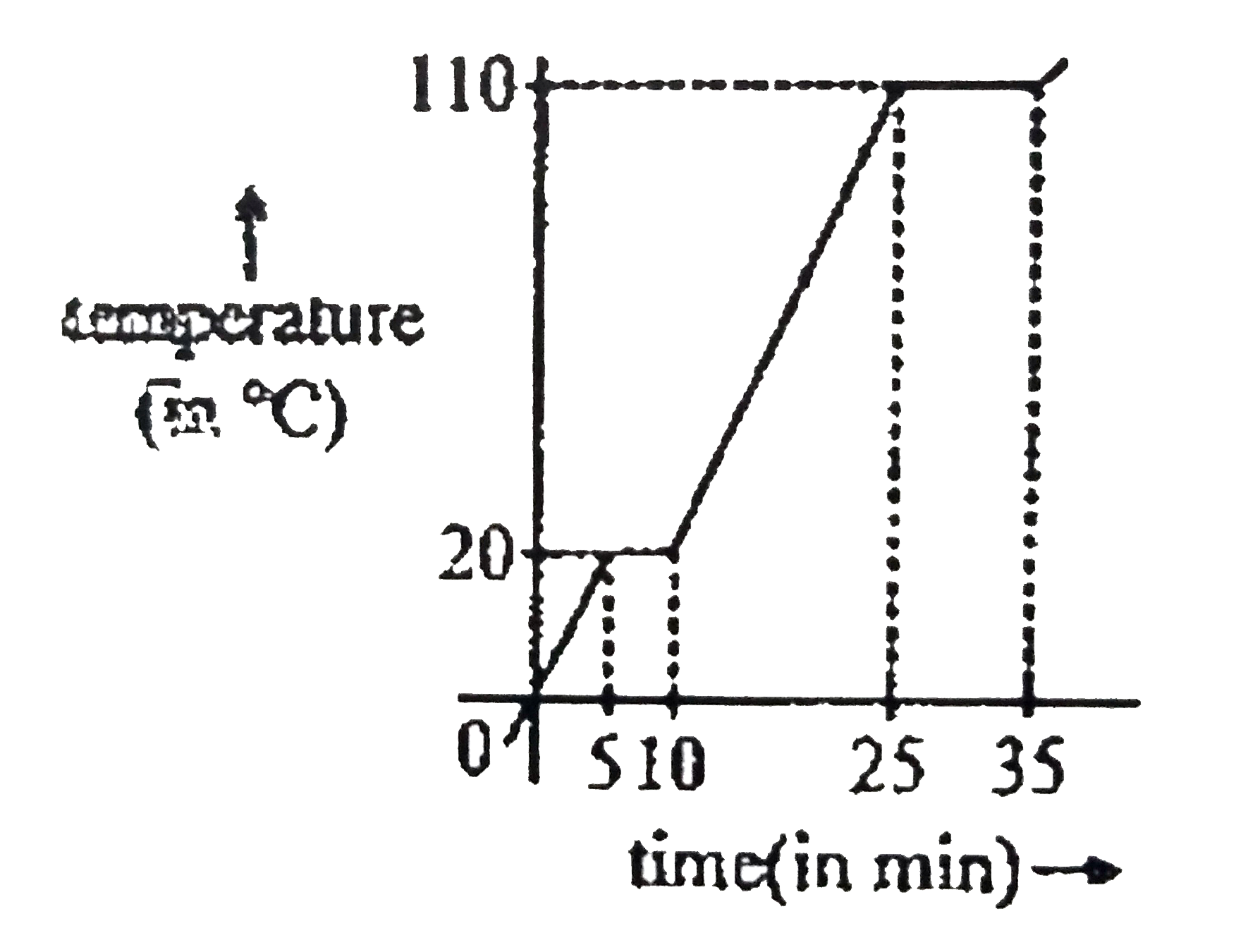
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- An experimentally decided formula for relation between pressure and de...
Text Solution
|
- One kg of a substance (initially solid of 0^(@)C) is supplied heat at ...
Text Solution
|
- One kg of a substance (initially solid of 0^(@)C) is supplied heat at ...
Text Solution
|
- One kg of a substance (initially solid of 0^(@)C) is supplied heat at ...
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of equal of length are joined to from an equilateral triang...
Text Solution
|
- A force vecF=(-yhati+xhatj)N acts on a particle as it undergoes counte...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass m and radius R rest on a plank of mass 2m lyi...
Text Solution
|
- Shown in the figure is a system of three particles having masses m(1)=...
Text Solution
|
- An iron nail of mass 0.2 kg is dropped from a height h=1m from level o...
Text Solution
|
- An advertisement claims that a certain 1200kg car can accelerate from ...
Text Solution
|
- Two men 'A' and 'B' are standing on a plank. 'B' is at the middle of t...
Text Solution
|
- The state of an ideal gas is changed through an isothermal process at ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas for which lambda=4//3, is heated at constant pressure. What perc...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along x-axis. The position of the particle at time t ...
Text Solution
|
- A force vecF=(3xy-5z)hatj+4zhatk is applied on a particle. The work do...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3 xx 10^(-6) m^(...
Text Solution
|
- In a figure shown mass of A and B is equal to M each. Friction between...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is dragged with same constant speed on two rough sur...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical rods which have thermally insulated lateral surface are...
Text Solution
|