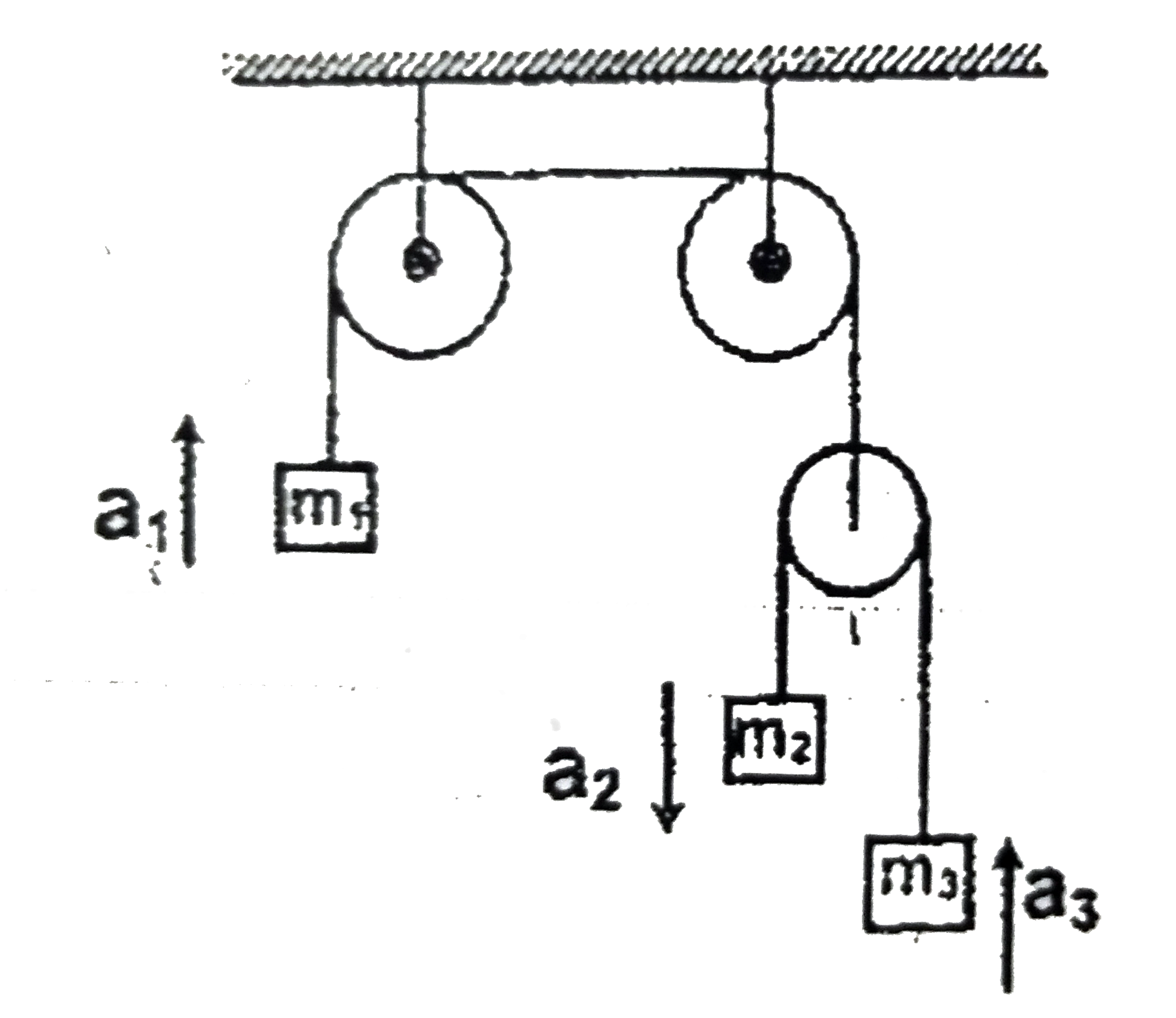
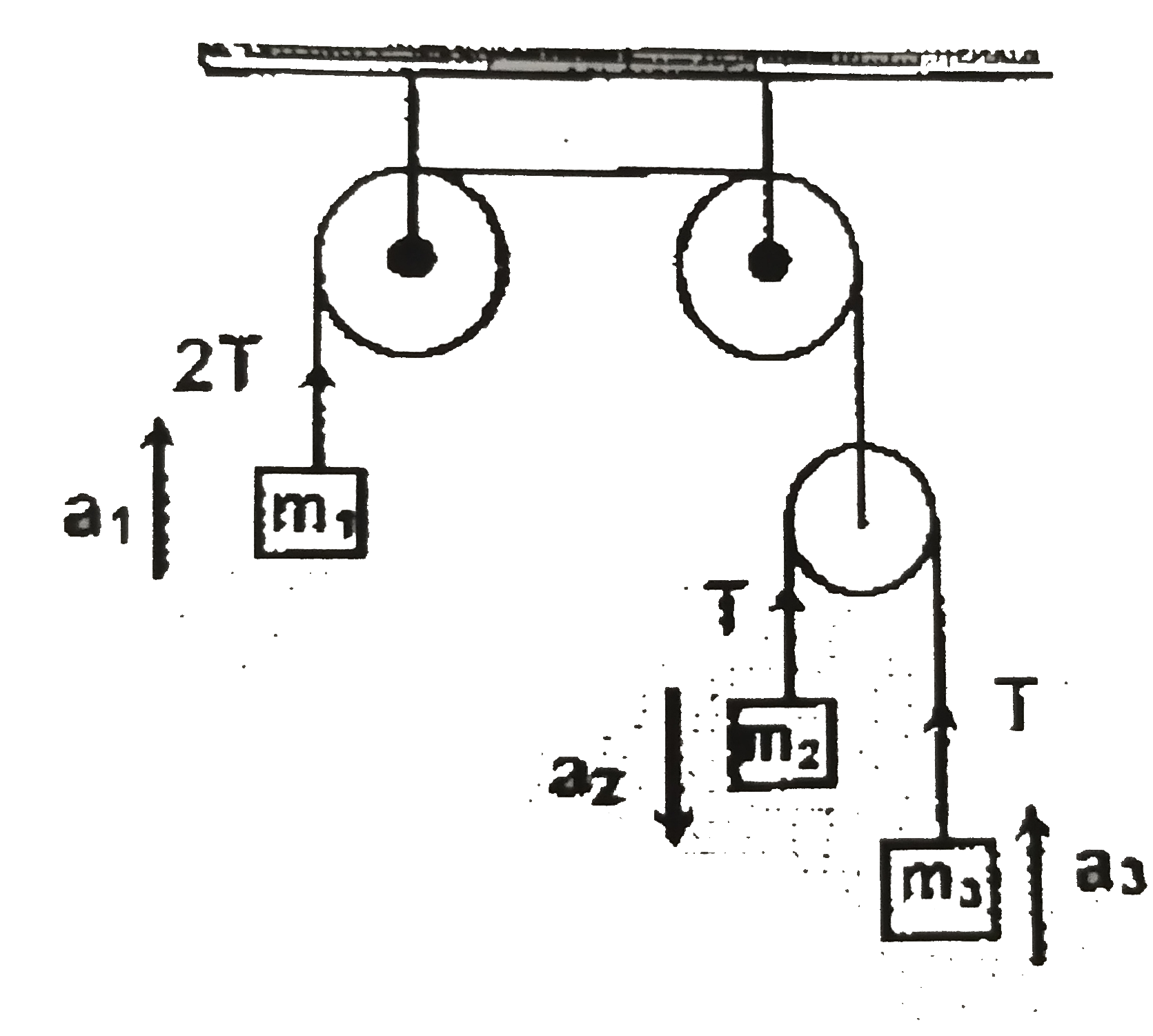
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- A particle leaves the origin with an initial velocity vecv=3hati m/s a...
Text Solution
|
- An equimolar mixture of a mono atomic and diatomic gas is subjected to...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure, all the pulleys are frictioniess and massless,...
Text Solution
|
- A person vibrates the end of a string sending transverse waves down th...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods AB, BC and BD of same length l and cross-sectionsl area A ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 2 kg and 4kg are connected through a massless ine...
Text Solution
|
- A block is hanged by means of two identical wires having cross section...
Text Solution
|
- The average power transmitted by a progressive wave in term of standar...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 kg piston encloses 32 g of oxygen gas at a temperature of 27^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls of masses 1 kg each are connected by an inextensible massles...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods are joined between fixed supports as shown in the figure. Con...
Text Solution
|
- Power radiated by a black body is P0 and the wavelength corresponding ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is subjected to a force vecF=F(0)[cos (t)hati+sin...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure verus Volume graphs for two process for ideal gas is shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the adjacent figure. The cube shaped 0.46 carrage ABCDEFGH of...
Text Solution
|
- A car is acclerating down on an inclined plane as shown in the figure ...
Text Solution
|
- In travelling transverse wave in string for a small element
Text Solution
|
- A substance of mass M kg requires a power input of P wants to remain i...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m kept at the origin is subjected to a froce vecF=(...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length l is rotating with constant angular...
Text Solution
|