A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-TEST PAPERS-PHYSICS
- Which of the following statements is/are incorrect
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m suspended by a string of length l revolves in a h...
Text Solution
|
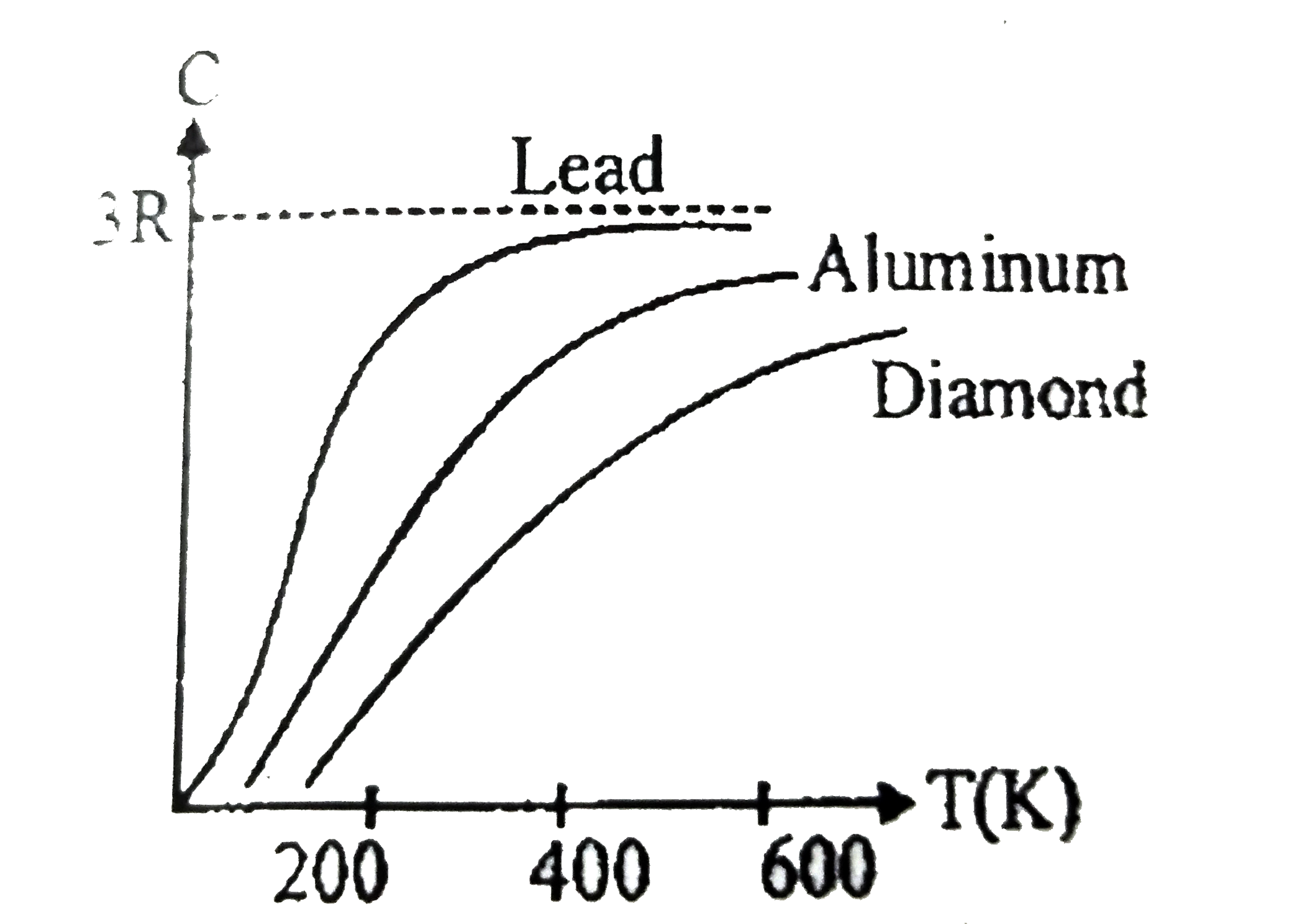
- According to Dulong & Petits law, molar heat capacity of solids at roo...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two frames of reference, S and S', the first one being fixed ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two frames of reference S and S', the first one being fixed t...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 3.14 kg is suspended from one end of a non uniform wire...
Text Solution
|
- Earth receives 1400 W//m^(2) of solar power. If all the solar energy f...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along x-axis. The position of the particle at time t ...
Text Solution
|
- A cone of radius r and height h is kept on a turntable rotating with a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rope of length 12m and mass 12kg hangs vertically from a rig...
Text Solution
|
- Two block-spring mass system are moving on smooth horizontal surface a...
Text Solution
|
- An elastic string has a force constant k and mass m. the string hangs ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass 1kg and length 6.25 m is hinged at one end of a smooth h...
Text Solution
|
- Find longest wavelength in Lyman series of hydrogen atom spectrum.
Text Solution
|
- The de-Broglie wavelength of an electron moving in the nth Bohr orbit ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the half life period of a radioactive substance if its activ...
Text Solution
|
- The total energy of eletcron in the ground state of hydrogen atom is -...
Text Solution
|
- A heshly prepared radioactive source of half life 2 hrs emits radiatio...
Text Solution
|
- The average current due to an electron orbiting the proton in the n^(t...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of the shortest orbit in a one electron system is 18 pm it...
Text Solution
|