Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-SECTION-B
- How does an electrostatic precipitator work to remove particulate poll...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given aquatic food chain and answer the questions that follo...
Text Solution
|
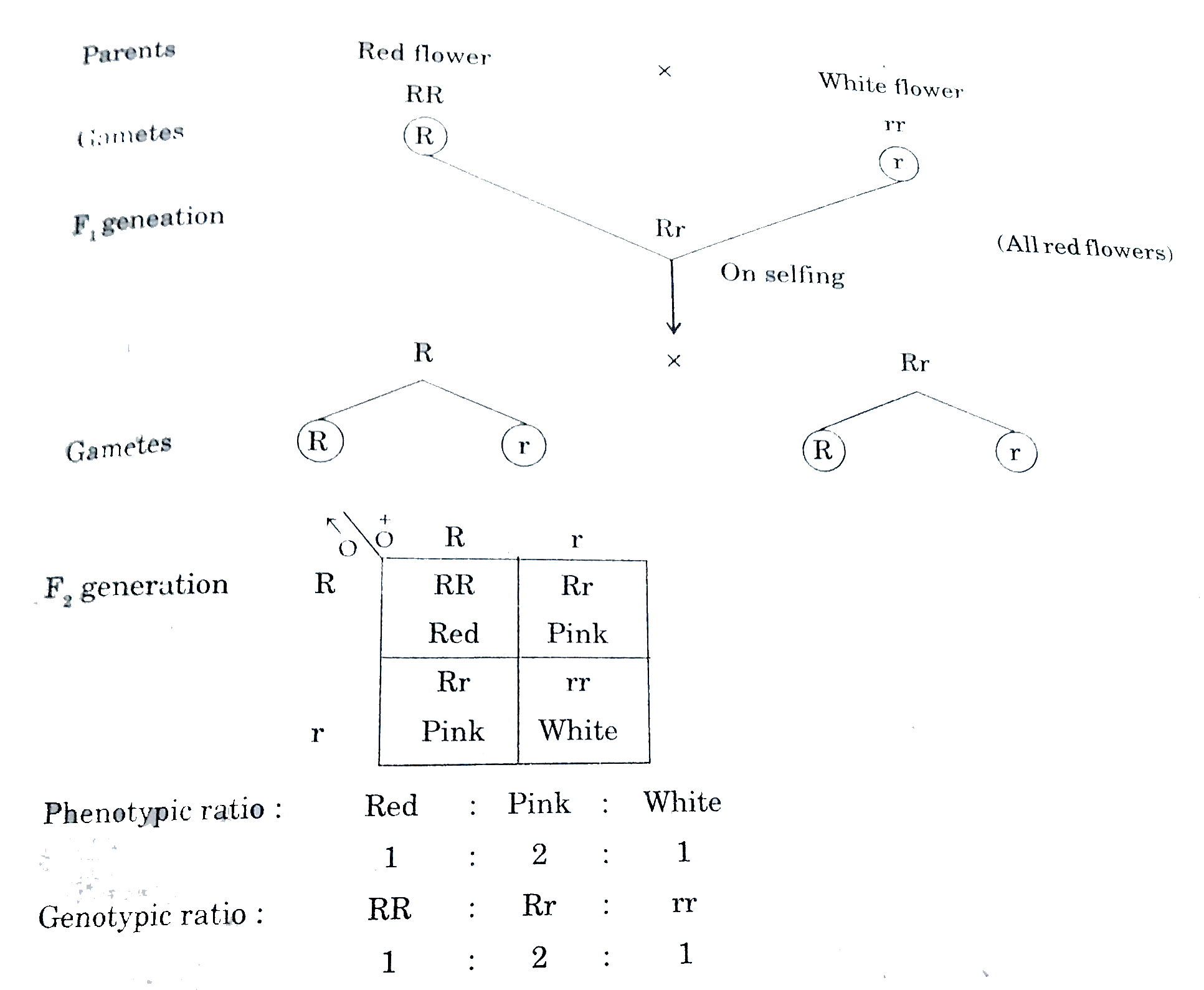
- Why are F(2) phenotypic and genotypic ratios same in a cross between r...
Text Solution
|
- Geitonogamous flowering plants are genetically autogamous but function...
Text Solution
|
- When and where do chorionic villi appear in humans ? State their funct...
Text Solution
|
- In a cross between two tall pea plants some of the offsprings produced...
Text Solution
|
- A student on a school trip started sneezing and wheezing soon after r...
Text Solution
|
- Name two commonly used bioreactors. State the importance of using a bi...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How does cleistogamy ensure autogamy? (b) State one advantage an...
Text Solution
|
- A mature, embryo-sac in a flowering plant may possess 7-cells, but 8-n...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the structure of a nucleosome.
Text Solution
|
- Mention the evolutionary significance of the following organisms : (...
Text Solution
|
- In an agricultural field there is a prevalance of the following organi...
Text Solution
|
- How does the applications of the fungal genus, Glomus, to the agricult...
Text Solution
|
- Plenty of algal bloom is observed in a pond in your locality. a) Wri...
Text Solution
|
- Mention the role of ribosomes in peptide-bond formation. How does ATP ...
Text Solution
|
- How do copper and hormone releasing IUDs act as contraceptives? Explai...
Text Solution
|
- If you squeeze a seed of orange you might observe many embryos of diff...
Text Solution
|
- A recombinant DNA is formed when sticky ends of vector DNA and foreign...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of polymerase...
Text Solution
|