Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
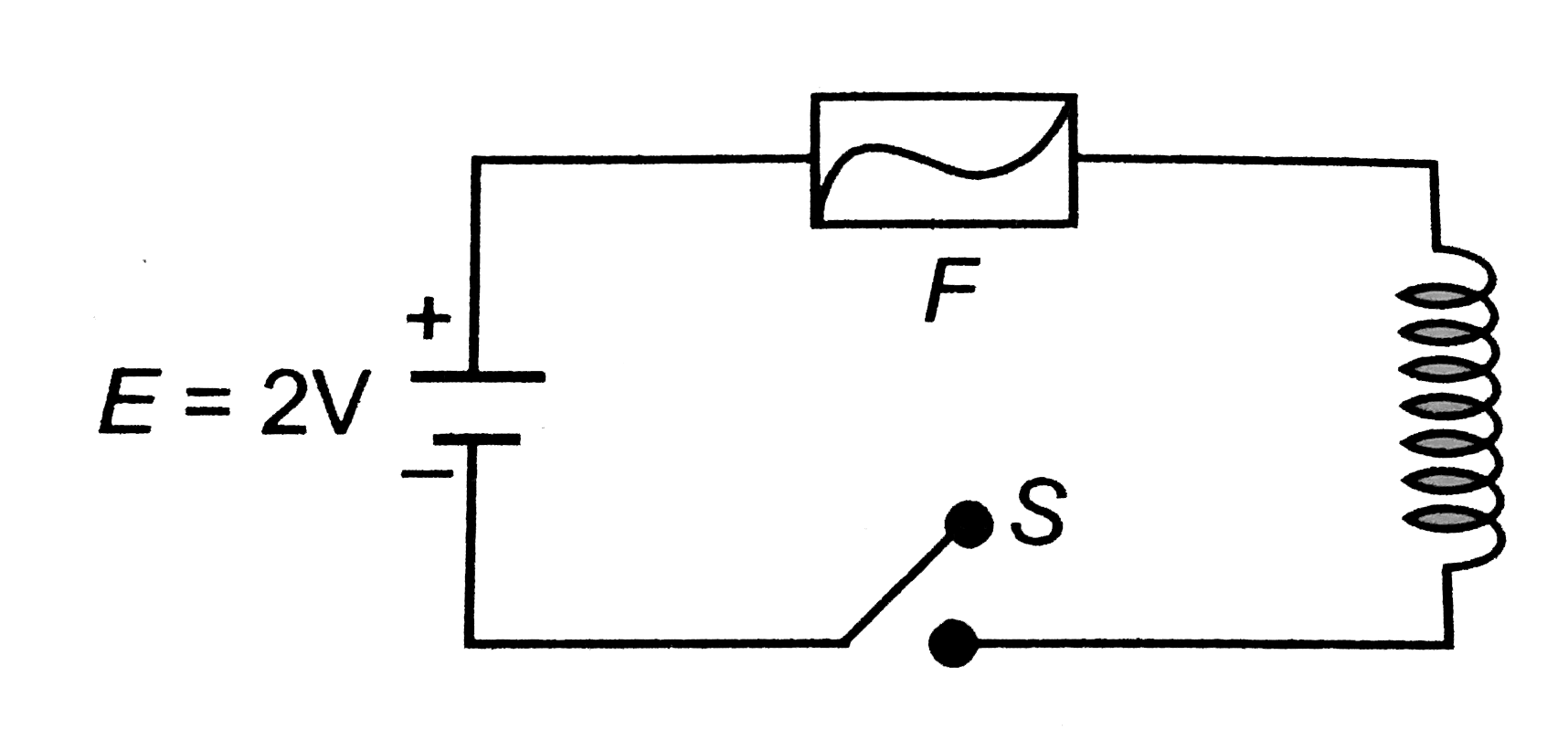
- In the circuit shown, the cell is deal. The coil has an inductance of ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shows Fig the cell is ideal. The coil has an inductance...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, the cell is deal. The coil has an inductance of ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a circuit consists of resistors, inductor, battery and a swit...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, the switch 'S' is closed at t = 0 . Then the cur...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, find the value of resistance R in terms of induc...
Text Solution
|
- A fuse wire with radius 1 mm blows at 1.5 amp . The radius of the fuse...
Text Solution
|
- A fuse wire of circular cross-section has a radius of 1mm. This wire b...
Text Solution
|
- Figure-5.362 shows a circuit in which an inductor of 5H is a=connected...
Text Solution
|