Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Find the acceleration of masses m(1), m(2) and m(3) shown in figure-2....
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown tension in string AB always lies between m(1)g and...
Text Solution
|
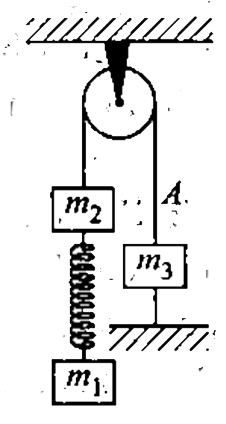
- Three blocks arranged with pullwy and spring as shown in fig. If the s...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected as shown in the figure...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks of masses m(1), m(2) and M are arranged as shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- In the given arrangement, all strings and pulleys are light. When the ...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in fig., all pulleys are mass less and the string ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of masses m(1), m(2) and m(3) shown in figure-2....
Text Solution
|
- In figure shown, pulley are ideal m(1) gt 2m(2) . Initially the system...
Text Solution
|