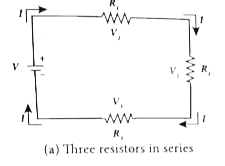
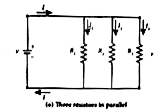
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Explain the equivalent resistance of a series and parallel resistor ne...
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent resistance of n identical resistors connected in parall...
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent resistance of two resistors connected in series 6Omega ...
Text Solution
|
- श्रेणी तथा समान्तर - क्रमो में प्रतिरोधों के संयोजन का तुल्य - प...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the equivalent resistance of a series and parallel resistor ne...
Text Solution
|
- Define effective resistance of a number of resistors connected in a se...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the equivalent resistance of a series and parallel resistor ne...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the equivalent resistance of a series and parallel resistor ne...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the equivalent resistance of a series and parallel resistor ne...
Text Solution
|