Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
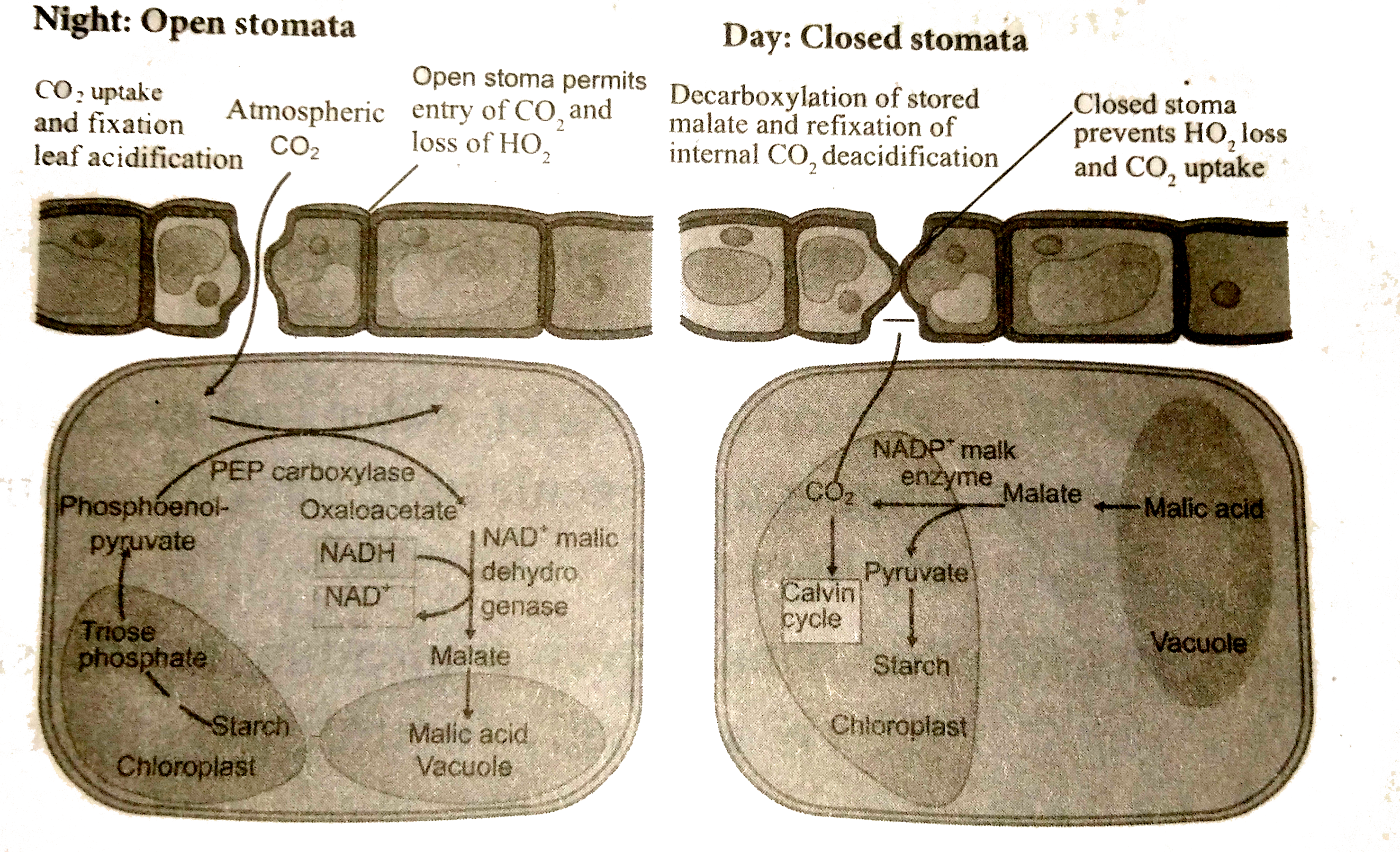
- Describe Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM Cycle).
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following kinds of plant fixes carbon dioxide by way of c...
Text Solution
|
- CAM উদ্ভিদের বিপাকীয় তাৎপর্য কী কী ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain in detail about Crassulacean Acid Metabolism.
Text Solution
|
- The C4 Pathway | Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (Cam)
Text Solution
|
- Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (Cam) | Photorespiration
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following kinds of plant fixes carbon dioxide by way of c...
Text Solution
|
- Describe : Tricarboxylic acid cycle OR describe Kreb's cycle
Text Solution
|
- Citric acid cycle is…….step in carbohydrate metabolism
Text Solution
|