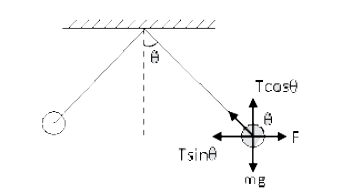
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE ADVANCED PREVIOUS YEAR-JEE (ADVANCE) 2020-SECTION 2
- A beaker of radius r is filled with water (refractive index (4)/(3...
Text Solution
|
- A student skates up a ramp that makes an angle 30^(@) with the horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and length L , pivoted at one of its ends, is hangin...
Text Solution
|
- In an X - ray tube , electrons emitted from a filament (cathode) ca...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical non - conducting solid spheres of same and charge are...
Text Solution
|
- Starting at time t = 0 from the origin with speed 1 ms^(-1) , a...
Text Solution
|