Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
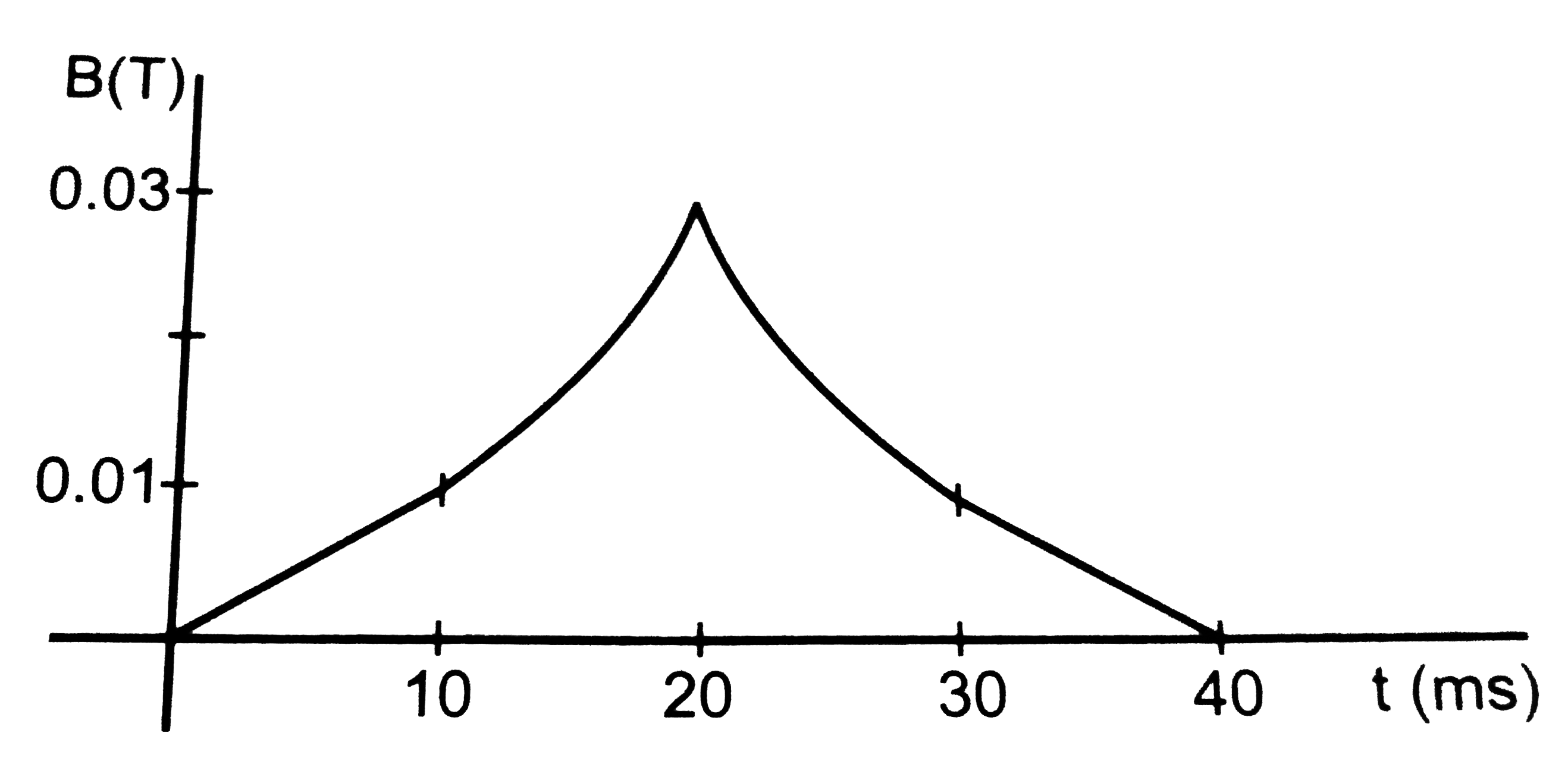
- (a) the magnetic field in a region varies as shown in . Calculate the ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic loop is placed in a nonuiform magnetic field. Will an emf b...
Text Solution
|
- A loop of wire enclosing an area S is placed in a region where the mag...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting square loop is placed in a magnetic field B with its plan...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform but time varying magnetic field is present in a circular reg...
Text Solution
|
- (a) The magnetic field in a region varies as shown in figure. Caculate...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting loop in the form of a circle is placed in a uniform magne...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular conducting loop of length l and breadth b enters a unifo...
Text Solution
|
- A single conducting loop with an area of 2.0 m^(2) rotates in a unifor...
Text Solution
|