Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise TRY YOURSELF|110 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-A) Objective Type Questions (Only one answer)|47 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT SECTION - D Assertion-Reason Type Questions|25 VideosGRAVITATION
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT SECTION - D (ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS)|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE -ASSIGNMENT SECTION - D
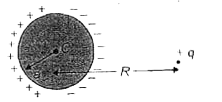
- A point charge +q is held at a distance R from the centre of an unchar...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by ...
Text Solution
|