A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN|Exercise CROSS PRODUCT|15 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-II AIPMT/NEET & AIIMS (2006- 2018)|6 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN|Exercise RESOLUTION OF VECTOR|8 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-V B|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS -DOT PRODUCT
- What is the angle between vecA and the resultant of (vecA + hatB) and...
Text Solution
|
- If ahati +bhatj is a unit vector and it iws perpendicular to hati +hat...
Text Solution
|
- Given that A=B. What is the angle between (vecA+vecB) and (vecA-vecB) ...
Text Solution
|
- The vector sum of two forces is perpendicular to their vector differen...
Text Solution
|
- A magnitude of vector vecA,vecB and vecC are respectively 12, 5 and 13...
Text Solution
|
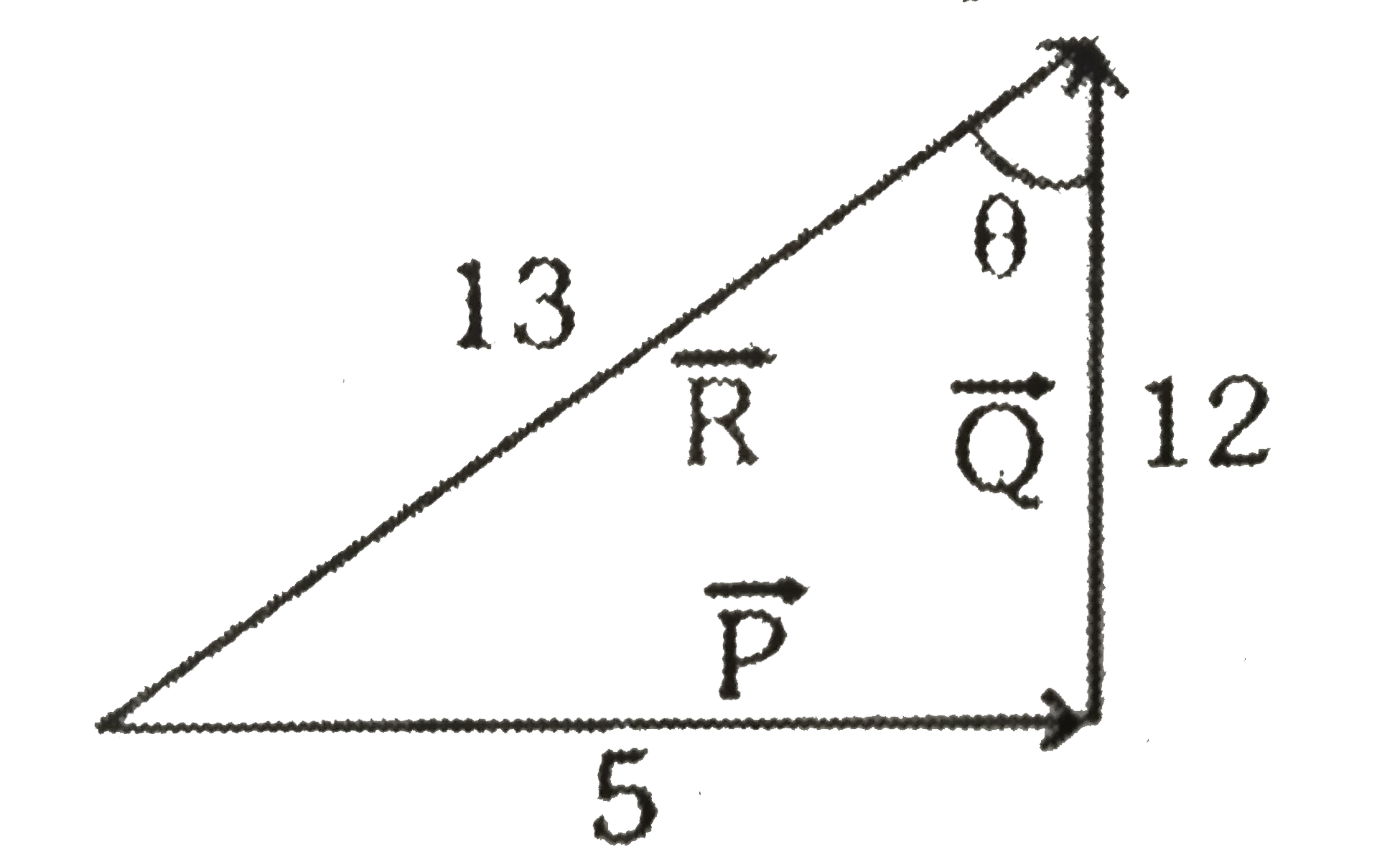
- If vectors vecP, vecQ and vecR have magnitudes 5, 12 and 13 units and ...
Text Solution
|
- A vector perpendicular to (4hati-3hatj) may be :
Text Solution
|
- A force (3hati+2hatj) N displaces an object through a distance (2hati-...
Text Solution
|
- If vecP.vecQ=PQ then angle between vecP and vecQ is
Text Solution
|
- The resultant of vecA and vecB is perpendicular to vecA. What is the a...
Text Solution
|
- What is the component of (3hati+4hatj) along (hati+hatj) ?
Text Solution
|
- The vector vecB= 5hati+2hatj-Shatk is perpendicular to the vector vec...
Text Solution
|
- What is the projection of vecA on vecB ?
Text Solution
|
- The angle between the vectors (hati+hatj) and (hatj+hatk) is
Text Solution
|
- The angles between the two vectors vecA=3hati+4hatj+5hatk and vecB=3ha...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec(A)=hat(i)A cos theta+hat(j)A sin theta, be any vector. Another...
Text Solution
|
- The vector vecP=ahati+ahatj+3hatj and vecQ=ahati-2hatj-hatk, are perpe...
Text Solution
|
- A force vecF= (3hati+4hatj) N acts on a body and displaces it by vecS=...
Text Solution
|
- The vector projection of a vector 3hat(i)+4hat(k) on y-axis is
Text Solution
|
- If a vector (2hati+3hatj+ 8hatk) is perpendicular to the vector (4hatj...
Text Solution
|