Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise In-Text Question-Evaluate Yourself|7 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions(M.C.Q)|38 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Textual Evaluation Solved(Choose the correct answer)|10 VideosHYDROGEN
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions Solved 5-Mark Questions|10 VideosPHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED (NUMERICAL PROBLEMS)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS -Textual Evaluation Solved( II brief question)
- Magnesium loses electrons successively to form Mg^(+),Mg^(2+)andMg^(3+...
Text Solution
|
- Define electronegativity .
Text Solution
|
- How would you explain the fact that the second ionisation potential is...
Text Solution
|
- Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is-2.18...
Text Solution
|
- The electronic configuration of atom is one of the important factor wh...
Text Solution
|
- In what period and group will an element with Z-118 will be present?
Text Solution
|
- Justify that the fifth period of the periodic table should have 18 el...
Text Solution
|
- Elements a,b,c and d have the following electronic configurations: ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the general electronic configuration of lanthanides and actides?
Text Solution
|
- Why halogens act as oxidising agents?
Text Solution
|
- Mention any two anomalous properties of second period elements.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the pauling method for the determination os ionic radius.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the periodic trend of ionisation potential.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the diagonal relationship
Text Solution
|
- Why the first ionisation enthalphy of sodium is lower than that of mag...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the ionic radii of K^(+) and Cl^(-) ions in KCl crystal. T...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following, give appropriate reasons. (i) Ionization po...
Text Solution
|
- What is screening effect ?
Text Solution
|
- Briefly give the basis for pauling's scale of electronegativity.
Text Solution
|
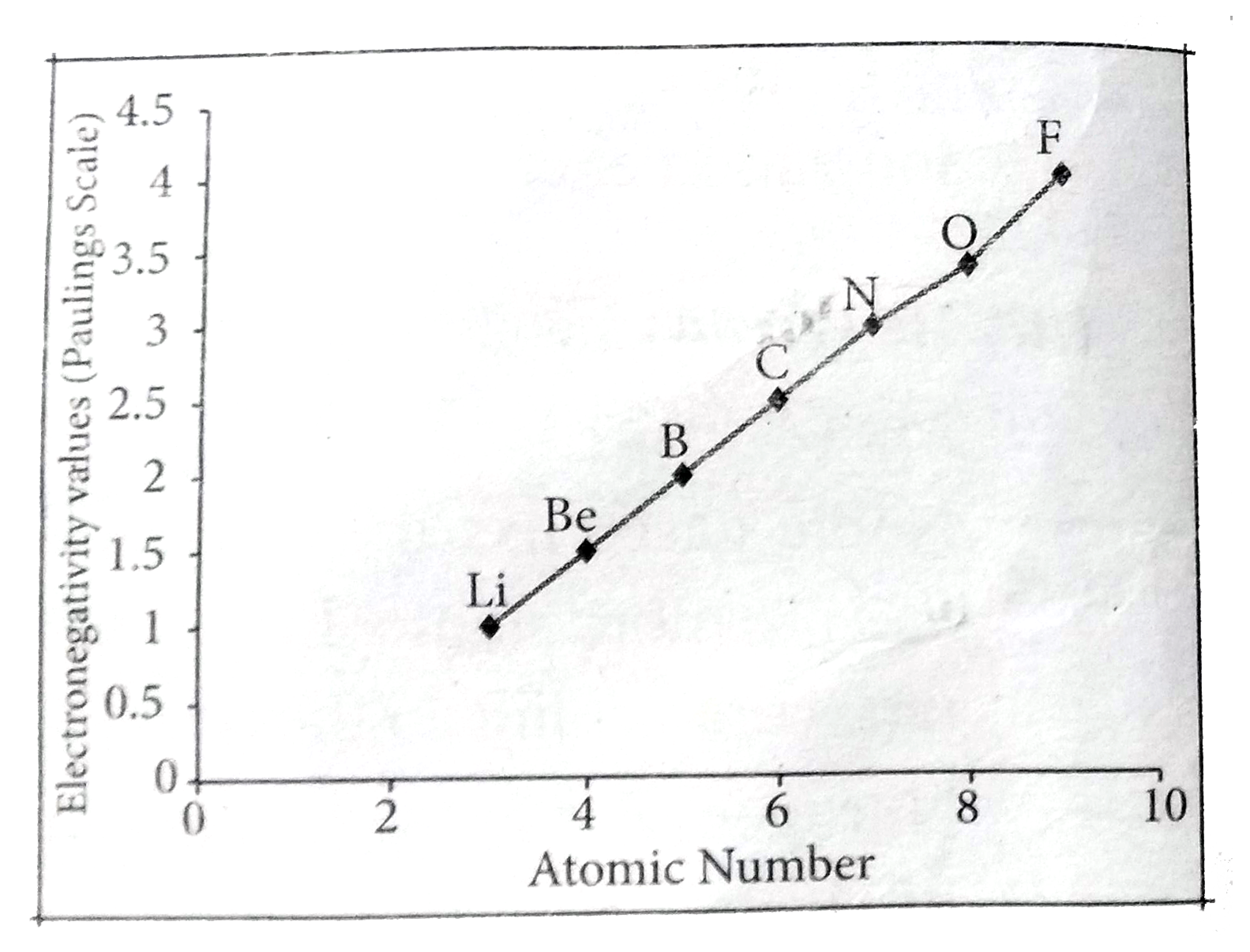
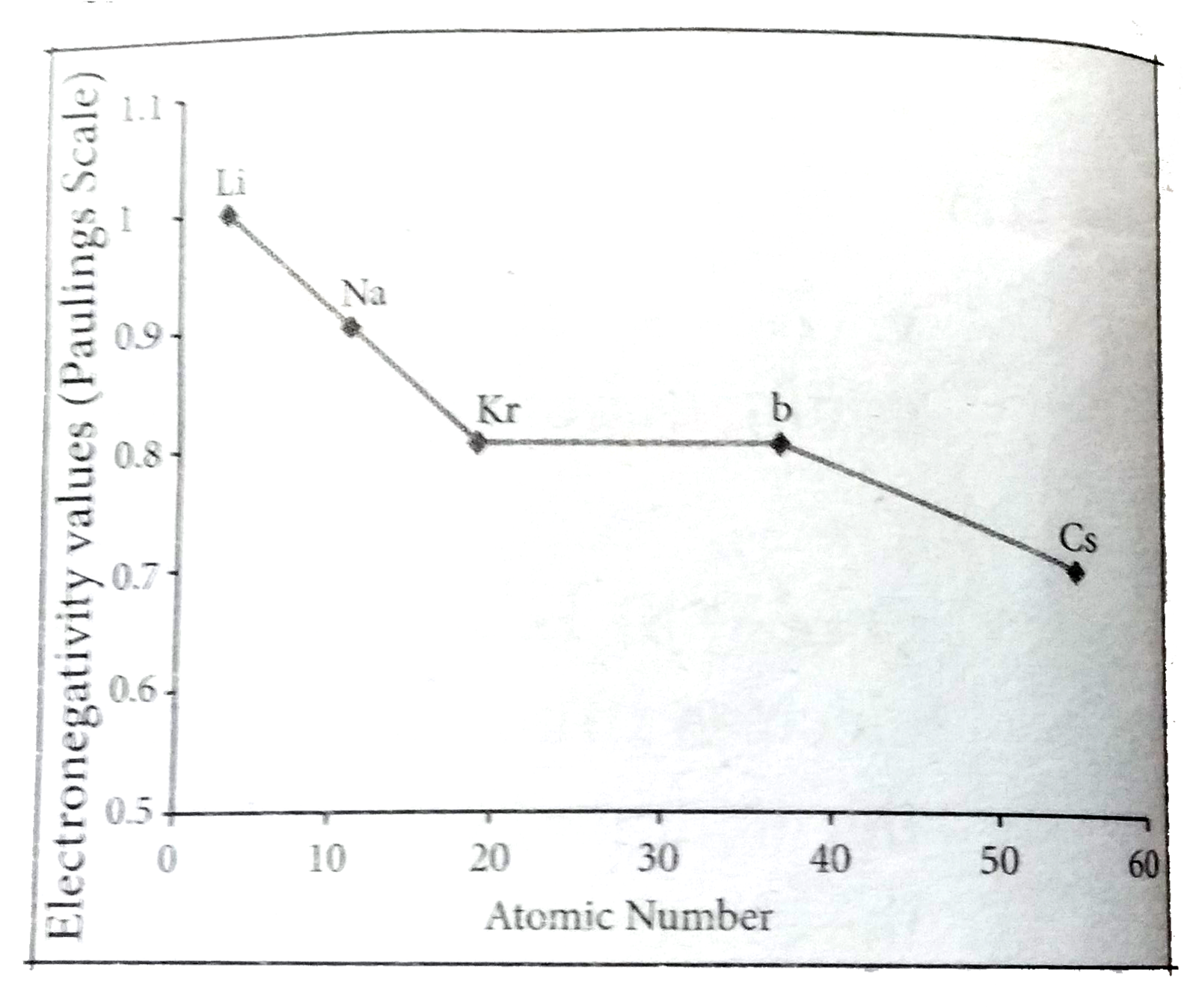
- State the trends in the variation of electronegativity in group and pe...
Text Solution
|