Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING
FULL MARKS|Exercise IN TEXT QUESTION-EVALUATE YOURSELF|10 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED (CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER.)|50 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED (5-MARK QUESTIONS)|14 VideosBASIC CONCEPTS OF ORGANIC REACTIONS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions Solved (5-Marks Question)|10 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED ( 5-Mark Questions )|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-CHEMICAL BONDING -TEXTUAL EVALUATION SOLVED (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS.)
- Draw MO diagram of CO and calculate its bond order .
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by interphase ?
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the formation of N2, molecule using MO Theory.
Text Solution
|
- What is dipole moment ?
Text Solution
|
- Linear form of carbondioxide molecule has two polar bonds. Yet the mol...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the Lewis structures for the following species. HNO(3)
Text Solution
|
- Explain the bond formation in BeCl(2) and MgCl(2).
Text Solution
|
- Which bond is stronger sigma or pi? Why ?
Text Solution
|
- Define bond energy.
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen gas is diatomic where as inert gases are monoatomic - explain...
Text Solution
|
- What is polar covalent bond? Explain with example.
Text Solution
|
- Considering x-axis as molecular axis, which out of the following will ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain resonance with reference to carbonate ion. Lewis structur...
Text Solution
|
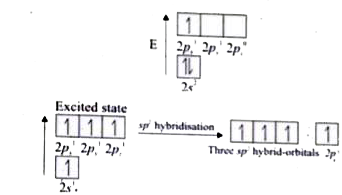
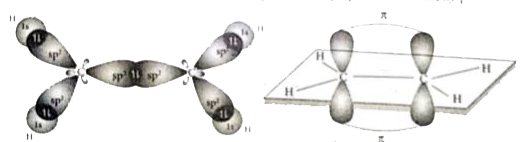
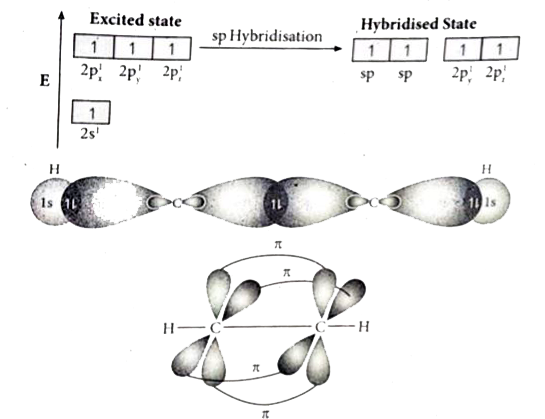
- Explain the bond formation in ethylene and acetylene.
Text Solution
|
- What type of hybridisations are possible in the following geometeries ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain VSEPR theory . Applying this theory to predict the shapes of I...
Text Solution
|
- CO(2) and H(2)O both are triatomic molecules but their dipole moment ...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following has highest bond order? N(2), N(2)^(+) or N...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the covalent character in ionic bond.
Text Solution
|
- Describe fajan's rule.
Text Solution
|