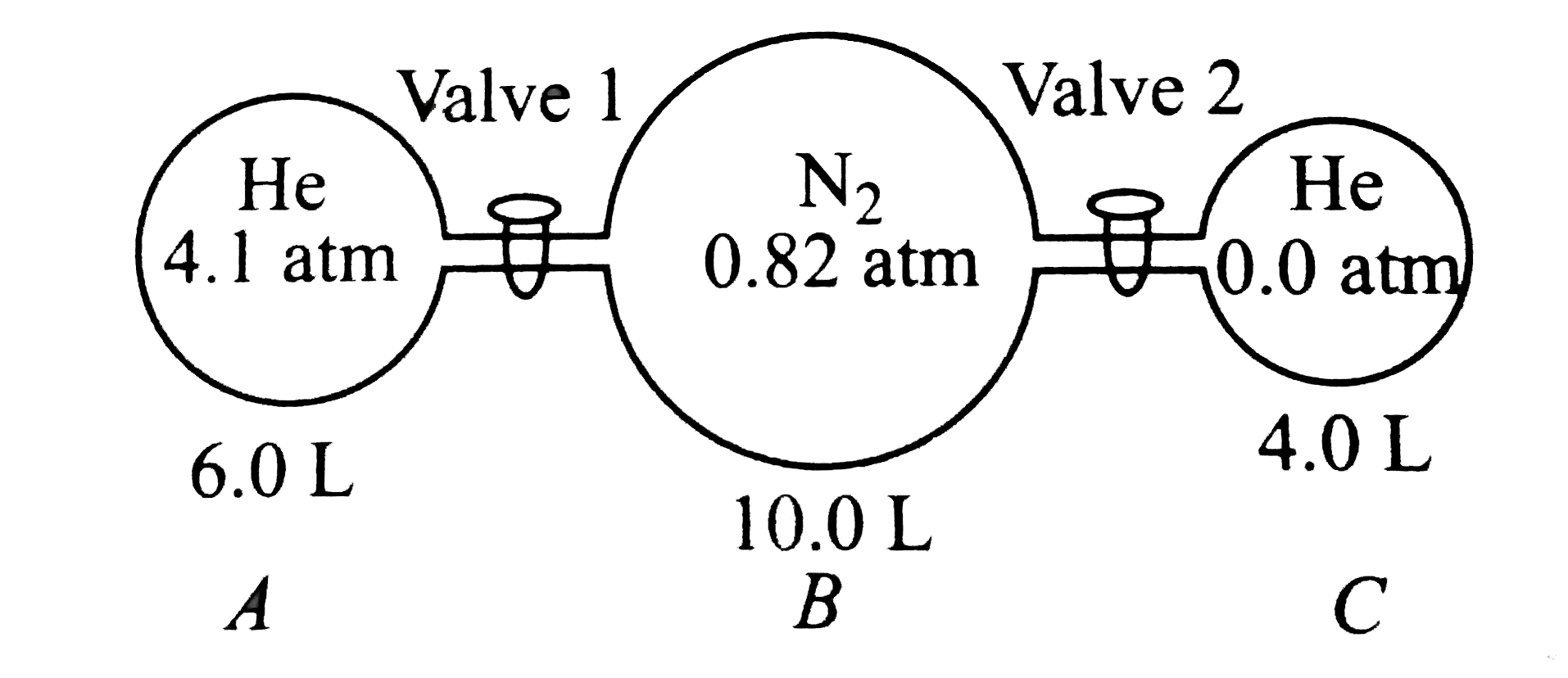Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The figure given below shows three glass chambers that are connected b...
Text Solution
|
- The figure given below shows three glass chambers that are connected b...
Text Solution
|
- The figure given below shows three glass chambers that are connected b...
Text Solution
|
- The figure given below shows three glass chambers that are connected b...
Text Solution
|
- In a thermally isolated system, two boxes filled with an ideal gas are...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram given below shows three glass chambers that are connected ...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram given below shows three glass chambers that are connected ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In joint diastole, all the four chamber of heart are in r...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a diagram to show the internal structure of human heart. Label on...
Text Solution
|