Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
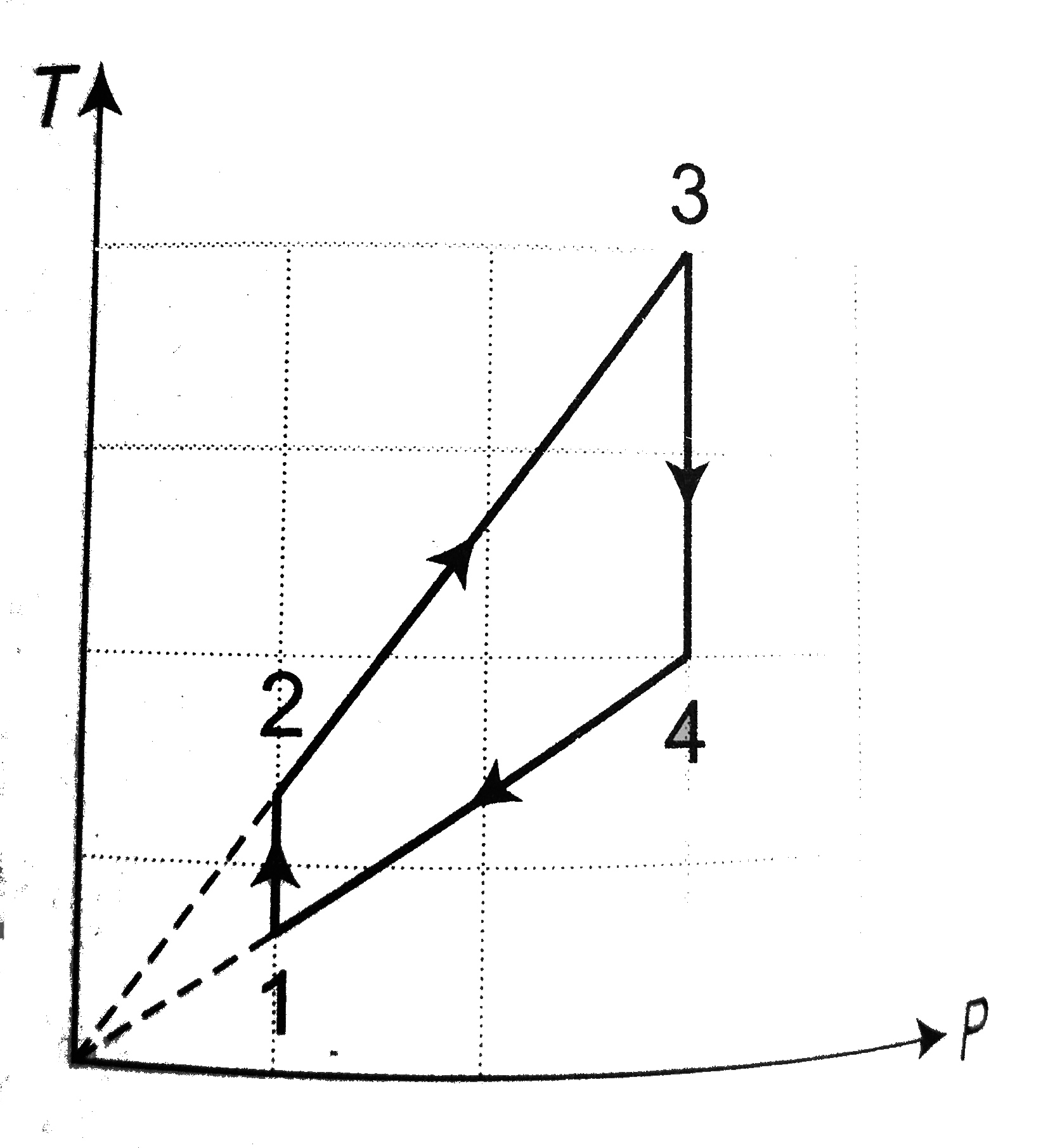
- Two moles of an ideal mono-atomic gas undergo a cyclic process as show...
Text Solution
|
- The moles of an ideal monoatomic gas perform a cycle shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas per form a cyclic as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal mono-atomic gas undergo a cyclic process as show...
Text Solution
|
- Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas per form a cyclic as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- 3 moles of an ideal mono atomic gas performs a cycle as shown in fig. ...
Text Solution
|
- n moles of an ideal gas is taken through a four step cyclic process as...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process as show...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA a...
Text Solution
|