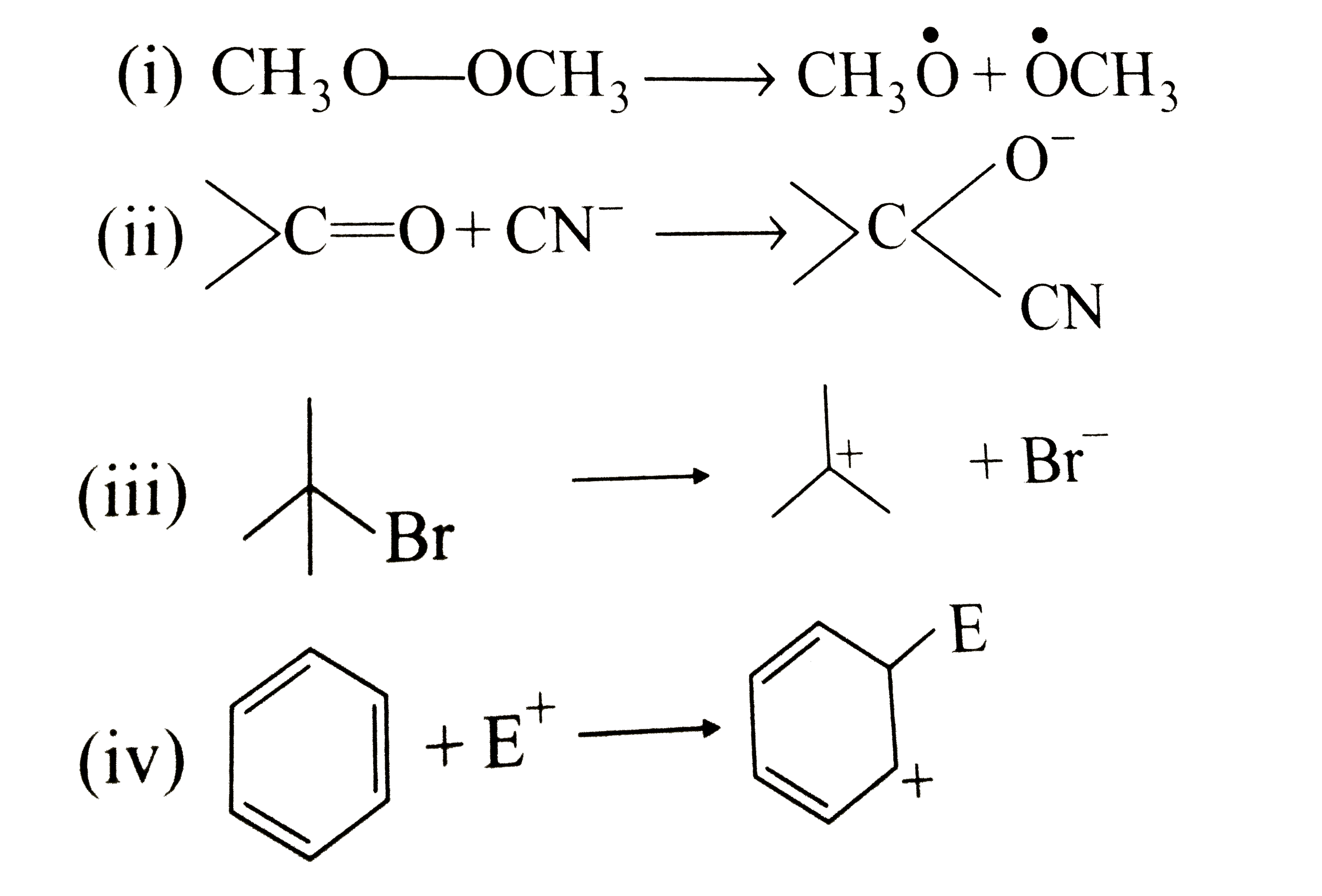
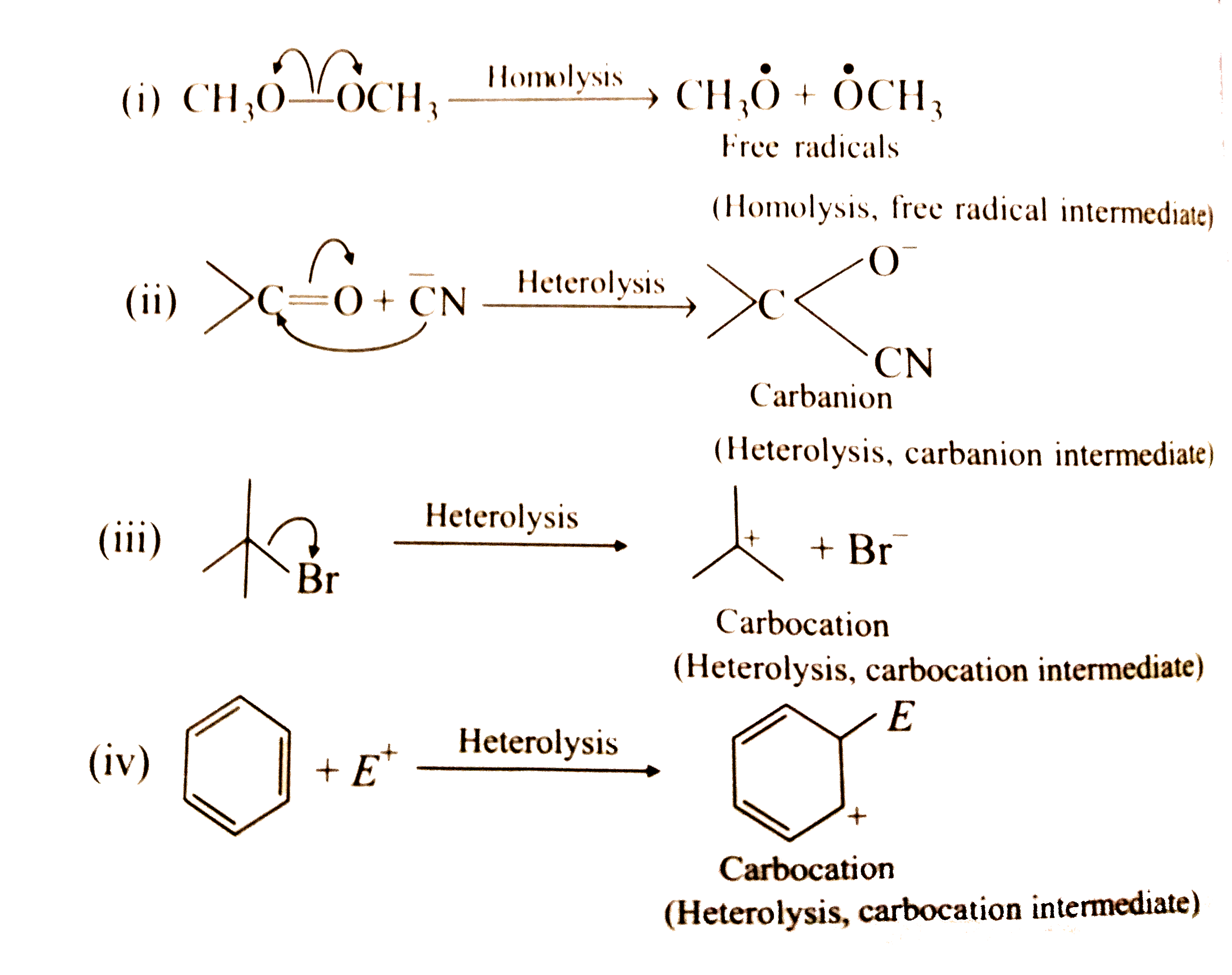
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)
OP TANDON|Exercise BRAIN STORMING PROBLEMS|14 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)
OP TANDON|Exercise OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (Level-A)|193 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)
OP TANDON|Exercise ILLUSTRATIONS OF OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS|20 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES
OP TANDON|Exercise SECTION V INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTION|3 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
OP TANDON|Exercise Integer|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OP TANDON-BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (MECHANISM OF ORGANIC REACTIONS)-PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE
- Classify the following into electrophilic and nucleophilic reagents: ...
Text Solution
|
- For the following bond cleavages, use curved arrows to show the electr...
Text Solution
|
- Identify each of the following as carbon-intermediates: {:((a)CH(3)-...
Text Solution
|
- Classsify the following reactions by type:
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following according to their stability: CH(3)CH(2)CH(2)o...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following : (a) How many types of fission are possible of...
Text Solution
|
- Explain: (i) Why trichloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid? ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following and identify the type for the inter-mediate spe...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following and identify the type of displacement reactions...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following addition reactions through the intermediate for...
Text Solution
|
- What are the various alkanes obtained due to insertion when 2-methylbu...
Text Solution
|
- Suggest a possible mechanism for the formation of R-Li from R-X by equ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the major E(1) product of the following reactions :
Text Solution
|
- Give possible mechanism of the given reaction using carbocation rearra...
Text Solution
|
- Which the resonance structure of the following species : (i) :overse...
Text Solution
|
- Which one hydrolysis at a faster rate by S(N)1 mechanism?
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|