Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
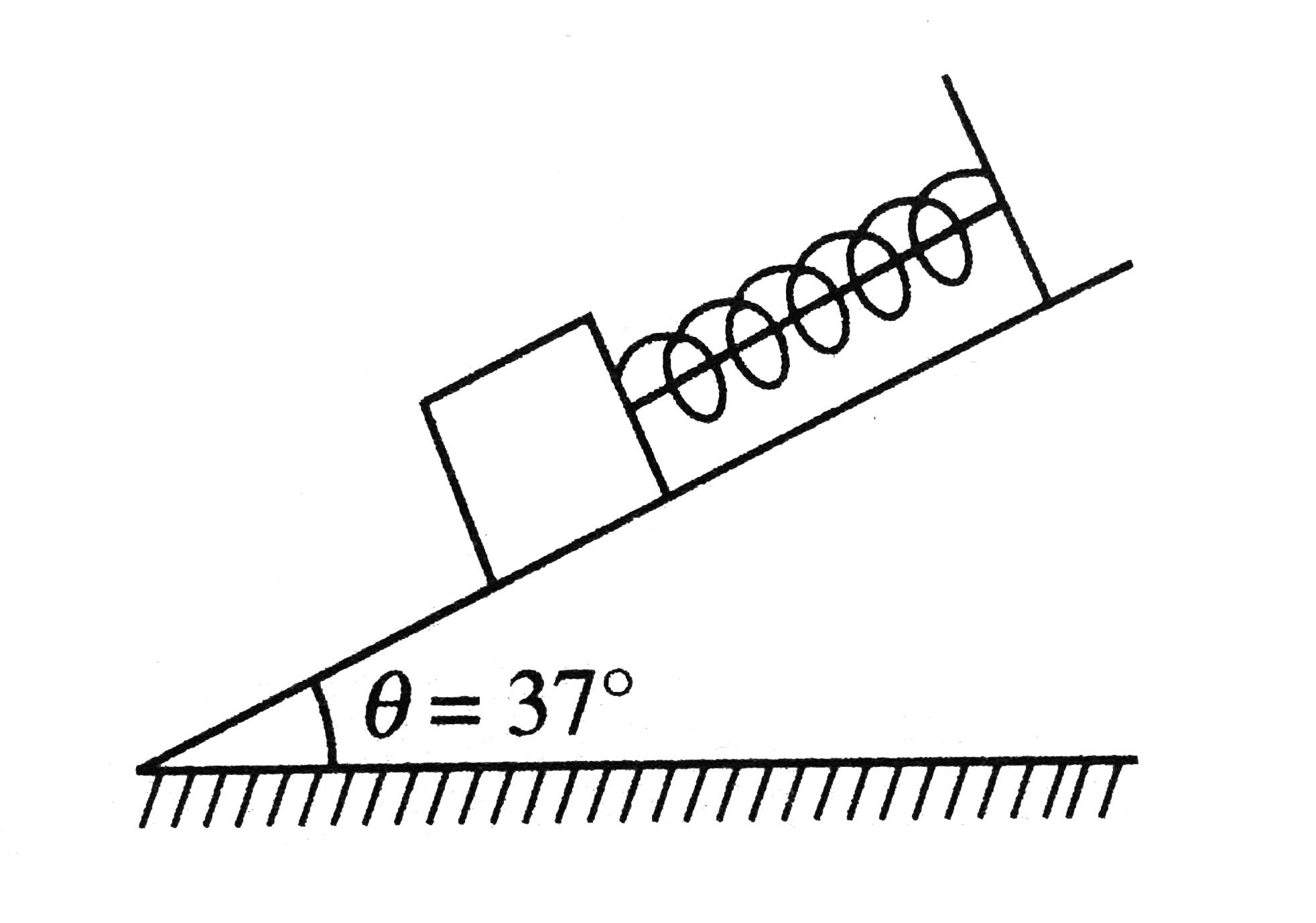
- A small block of mass m=1kg is attached with one end of the spring of ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is attached to one end of a mass less spring of spri...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass m=5kg is attached with a spring having force constan...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m=1kg is attached with one end of the spring of ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, a spring of spring constant K is fixed at on end ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a block of masss m is atteched at ends of two spri...
Text Solution
|
- Figure. shows a rough horizontal plane which ends in a vertical wall, ...
Text Solution
|
- A block ofmass m is attached with a spring in its natural length, of s...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is released when the spring was in its natrual len...
Text Solution
|