Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
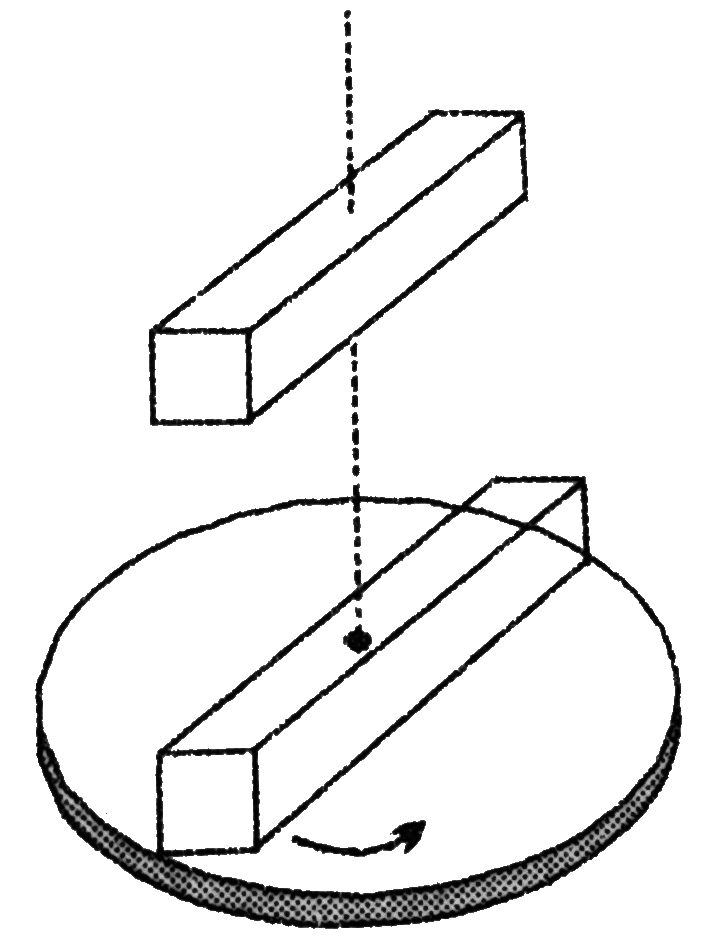
- A uniform disk turns at 2.4 rev//s around a frictionless axis. A nonro...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disk turns at 2.4 rev//s around a frictionless axis. A nonro...
Text Solution
|
- A disk with moment of inertia I1 rotates about frictionless, vertical ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid unifrom disk of mass m and radius R is pivoted about a horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disk of mass 300kg is rotating freely about a vertical axis ...
Text Solution
|
- त्रिज्या R की एक वृत्ताकार डिस्क का एक चौथाई भाग काटकर, इस भाग को मूल ...
Text Solution
|
- किसी एकसमान वृत्ताकार डिस्क ( चकती ) का जड़त्व आघूर्ण अधिकतम होगा, यदि ...
Text Solution
|
- Two disks are rotating about the same axis. Disk A has a moment of ine...
Text Solution
|
- A solid disk rotates in the horizontal plane at an angular velocity of...
Text Solution
|