Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-SET - II
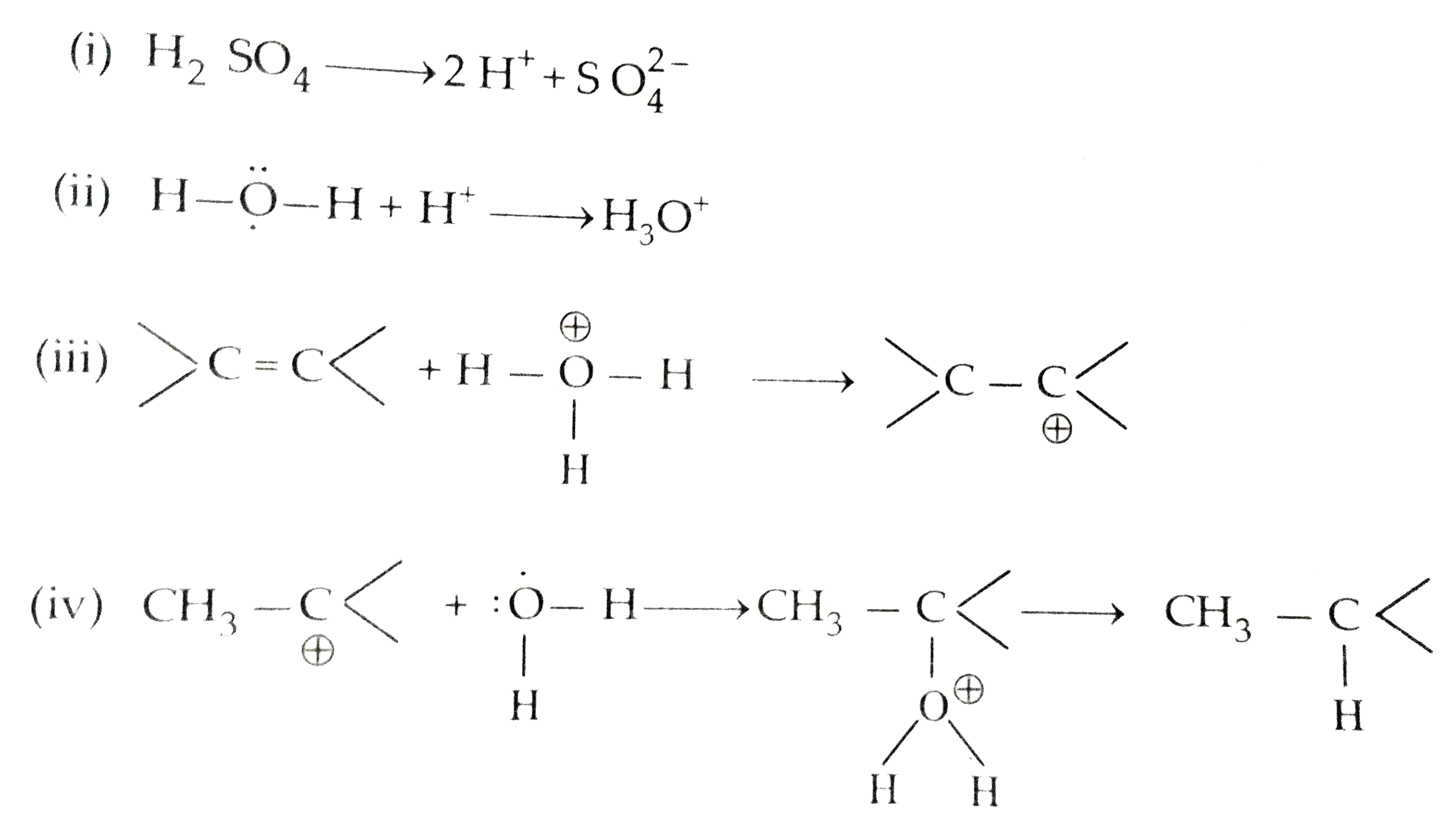
- Explain the mechanism of acid catalysed of an alkene to form corresp...
Text Solution
|
- What are lyophobic colloids? Give one example for them.
Text Solution
|
- Why is thie that only sulphide ores are connectrated by forth floata...
Text Solution
|
- Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds:
Text Solution
|
- Darw the structure of 2,6 Dimethyphenol.
Text Solution
|
- Rerrange the following in an increasing order of their basic strength...
Text Solution
|
- In corundum, oxide ions are arranged in hexagonal close packing and al...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the equilibrium constant K(c) for the rections. 3Sn^(4) ...
Text Solution
|
- Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain giving a suitable reason for each of the following : (i)...
Text Solution
|
- Write the main structural difference between DNA and RNA. Of the four ...
Text Solution
|
- What mass of NaCI ("molar mass" =58.5g mol^(-1)) be dissolved in 65g o...
Text Solution
|
- Write the stucture and names of all steresiomers fo the following com...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Differentiate between a disinfectant and an antiseptics. Given ...
Text Solution
|