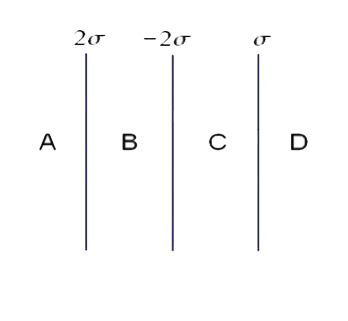
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CBSE MODEL PAPER-SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (THEORY)-Section – E
- a)State Gauss’s law in electrostatics. Show that with help of suitable...
Text Solution
|
- a) Define an ideal electric dipole. Give an example. b) Derive an ex...
Text Solution
|
- a) Derive the expression for the current flowing in an ideal capacitor...
Text Solution
|
- a) State the principle of ac generator. b) Explain with the help of ...
Text Solution
|
- a) Define a wave front. b) Draw the diagram to show the shape of pla...
Text Solution
|
- a) State two main considerations taken into account while choosing the...
Text Solution
|