Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
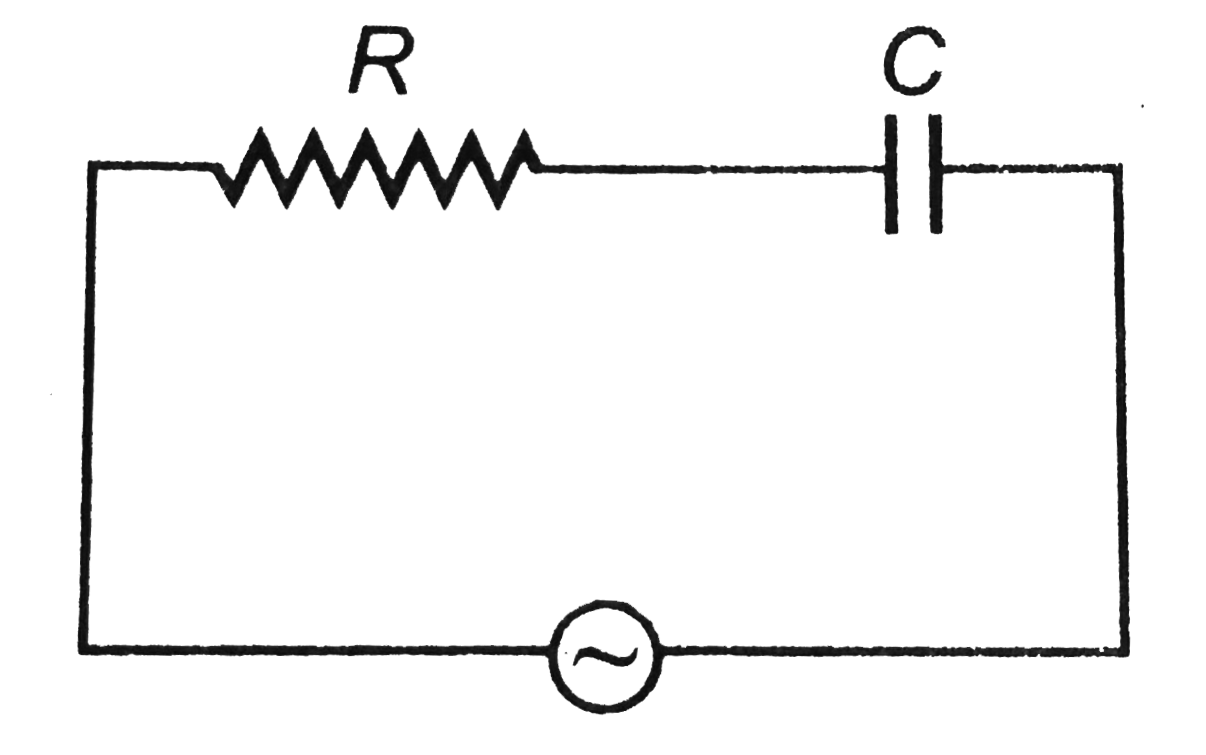
- A 50 Hz AC source of 20 V is connected across R and C as shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- A 50 Hz AC source of 20 V is connected across R and C as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- In a series C-R circuit shown in figureure, the applied voltage is 10 ...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor R and the capacitor C are connected in series across an ac ...
Text Solution
|
- In an L-C-R circuit the AC voltage across R, L and C comes out as 10 V...
Text Solution
|
- In an L-C-R circuit, if V is the effective value of the applied voltag...
Text Solution
|
- An ac source of 50 V (r.m.s value) is connected across a series R - C ...
Text Solution
|
- [" An ac source of "50V" (r.m.s "],[" value) is connected across a "],...
Text Solution
|
- In an LCR series ac circuit , the voltage across each of the componen...
Text Solution
|